Contents:
Navigating the noise of emerging tech is exhausting. The trick isn’t chasing every new hype cycle, but doubling down on technologies that have actually graduated from “experimental” to “essential.” Augmented Reality (AR) is one of them.
Hardware constraints are finally disappearing. With the maturation of mobile chipsets and the arrival of dedicated headsets from Apple and Meta, bringing AR products to market is no longer a gamble — it’s a scalable strategy. Consumer confidence is high, making 2026 the ideal time to separate the gimmicks from the tools that drive revenue.
Augmented Reality Technology: The Past, Present, and Future
In 1901, author L. Frank Baum imagined a “character marker,” electronic glasses that would overlay data onto people. It took over a century, but high-fidelity passthrough cameras and real-time 3D rendering have finally made Baum’s vision possible.
AR is no longer just “immersive digital experiences.” It is a practical layer of intelligence over the real world. The technology has moved past the novelty phase and entered the mainstream workflow. For brands, the question is no longer “What is AR?” but “How quickly can we integrate it?”
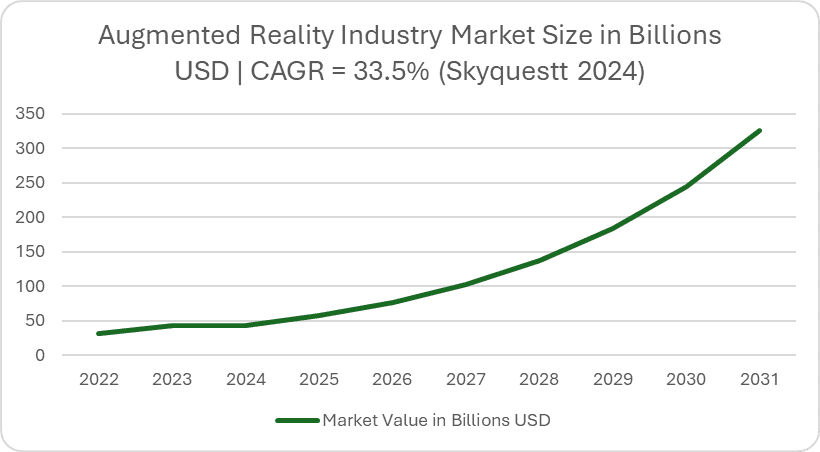
The market numbers back this up. SkyQuest reports that the global AR market is surging from $58.29B in 2024 to a projected $828.47B by 2033. That is a massive CAGR of 34.3%. This isn’t just growth; it is a clear signal that the demand for AR app development is shifting from “nice-to-have” to a standard business requirement.
13 Augmented Reality Trends in 2026 Table Summary
Check out the summary of 13 AR trends for 2026:
| # | Trend | Trend Summary | What It Means for Business |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Spatial Computing Platforms Shape the User Experience | UX shifts from “AR effects” to spatial workflows: anchored panels, persistent context, shared sessions—guided by platform conventions. | Differentiation comes from workflow design, not visuals. Teams that align with platform UI patterns ship faster and reduce UX friction. |
| 2 | AI in AR (Assistants + Scene Understanding) | AR becomes assistant-driven and more context-aware; AI improves perception (objects/surfaces/people/text) and guidance. | Lower support/training costs and higher task completion via guided, automated experiences (less menu navigation, more “do the next right thing”). |
| 3 | Photorealistic World Capture Pipelines | Faster, cheaper reality capture and photoreal scenes enable better digital twins without heavy manual modeling. | You can digitize spaces/products faster, enabling scalable training, sales enablement, inspection, and layout planning with lower content costs. |
| 4 | Interoperability via Open Standards | Common APIs and content standards reduce fragmentation across XR ecosystems. | Less vendor lock-in and cheaper multi-device support—better long-term ROI on XR roadmaps. |
| 5 | Privacy, Security, and “Bystander Trust” | Wearable cameras/mics elevate privacy expectations; trust failures block adoption. | Privacy UX becomes a feature, not a checkbox. Without governance, enterprise rollouts stall and consumer backlash risk rises. |
| 6 | AR Navigation and “AI Maps” | AR navigation and persistent anchors turn AR into location-aware, repeatable experiences (indoor/outdoor). | Enables persistent value (guidance, wayfinding, context) across visits—useful for campuses, retail, logistics, tourism. |
| 7 | AR in Manufacturing and Enterprise-Ready Spatial Devices | Strong ROI (training, maintenance, QC, safety), but requires environment-fit UX and IT governance. | AR becomes a real productivity tool only if it works with gloves/noise and fits enterprise controls (permissions, audits, distribution). |
| 8 | WebAR Helps Build More Accessible Experiences | Browser-based AR increases reach and reduces friction, but limits fidelity. | Faster time-to-market for marketing and lightweight product experiences; good for top-of-funnel and broad device coverage. |
| 9 | Augmented Reality in Marketing | Interactive AR campaigns improve brand metrics and engagement via try-on, demos, and contextual overlays. | Higher engagement and lift; AR becomes a repeatable growth lever when integrated with the funnel (not one-off stunts). |
| 10 | Augmented Reality in Healthcare | Hands-free overlays support training, procedures, visualization, and rehab; AR+ML aids detection workflows. | AR can improve training and reduce errors, but success depends on safety, validation, and compliance. |
| 11 | Augmented Reality in Retail and eCommerce | Try-on and visualization reduce uncertainty; in-store smart mirrors and mobile try-on improve conversion. | Improved conversion and lower returns; AR becomes part of the standard shopping UX for competitive categories. |
| 12 | Augmented Reality in the Automotive Industry | AR supports sales visualization, remote assistance, parking/driver monitoring, and HUD-style interfaces. | Shorter sales cycles and better service; in-vehicle AR requires strict safety UX and prioritization. |
| 13 | State of the Metaverse and Social AR | Metaverse hype cooled, but social presence and co-experiences remain valuable and practical. | Opportunity is in targeted social value (events, learning, support), not building “the metaverse.” Trust fundamentals are decisive. |
Trend #1: Spatial Computing Platforms Shape the User Experience (visionOS-like “Spatial UI”)
According to Apple, visionOS offers widgets that can be integrated into the user’s space, meaning that the user interface becomes part of the space rather than just a flat overlay. For platform context, see: Apple Vision Pro and Android XR.
What this means for businesses: Product value is shifting from “AR effects” to spatial workflows (anchored panels, persistent context, shared sessions) based on platform conventions.
How to Implement the Spatial Computing Platforms Trend in AR
Start with 1–2 spatially oriented workflows (training, remote support, planning) and design the user interface as anchored objects with:
- Persistence rules (when content remains and when it is reset)
- Collaboration status (who can see/edit what)
- “Elegant fallback” when functions/devices differ
Trend #2: AI in AR (Assistants + Scene Understanding)
AI is driving AR forward in two directions simultaneously: (1) assistant-driven experiences and (2) better perception of the real world.
AI Assistants in AR (Multimodal, Context-Aware, Action-Oriented)
According to Google, Android XR glasses paired with Gemini can see and hear what you are doing and provide you with information exactly when you need it — driving AR toward task management and automation.
What this means for businesses: The user interface becomes “assistant-driven” (instructions, verification, data entry, troubleshooting) instead of user-driven menu navigation.
AI as a Driver for AR Technologies (Core Perception)
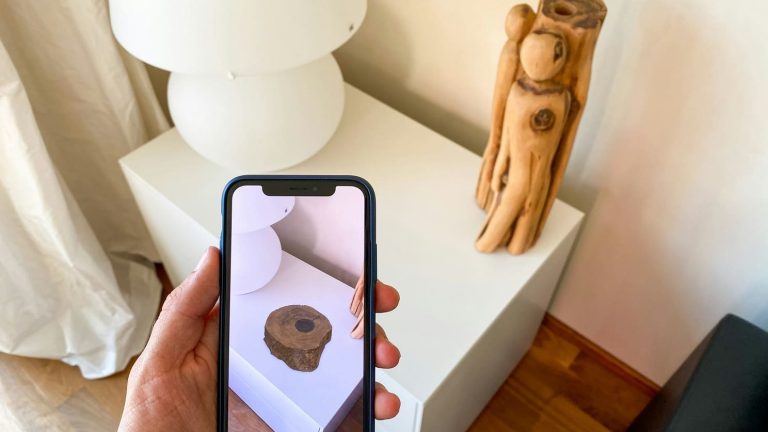
AI has always been used in AR to understand scenes. For example, object and surface recognition are crucial for applications such as Ikea’s AR Room Scanning App. This allows AR programs to recognize objects in the real world and overlay them with 3D elements or provide the user with contextual information.
Another important example is scanning people: AI and AR are used to recreate human faces and bodies. A notable example of this is Apple Vision Pro’s digital “persona” feature, which scans your face to use it for FaceTime calls while you’re wearing the headset.
Text recognition has also become established. With the Google Translate app, you can point your smartphone at text in any language and get a real-time translation displayed as an overlay.
Case Study: Combining AI and AR for Device Setup and Troubleshooting
With MobiDev, you can develop a product setup application to demonstrate how AI and AR can simplify internet router setup. Using a smartphone camera, users see 3D instructions for setting up the router. The app can also help diagnose simple issues with 3D visualizations in augmented reality. This proof of concept relies on the 3 following features:
- Recognizing the router itself
- Identifying the cables that need to be connected
- Understanding the indicators on the front of the router to determine the status of the device
This application goes one step further than other similar AR remote support applications by reducing the need for human interaction.
The Future of AI in AR
There are signs of a more generative future for AI in AR. For example, Spline is a tool that can be used to generate 3D objects using natural language. This would make it possible to develop 3D objects, textures, and animations for AR experiences entirely through simple voice commands.
How to Implement AI in the AR Trend
There are 3 key steps to take:
- Identify “help moments” in your process (where users hesitate or make mistakes).
- Connect to an approved knowledge base (SOPs, manuals, catalogs).
- Deliver an assistant-driven UX (short prompts, confirmations, voice/gestures) with strict privacy controls and audit logs.
Trend #3: Photorealistic World Capture Pipelines (Gaussian Splatting/NeRF, Photogrammetry)
Photogrammetry is already widely used in AR pipelines. Gaussian splatting and NeRF are often “cooler” for photorealistic captures, but typically require more power and optimization for real-time AR. Nevertheless, they are worth keeping an eye on as the tools improve.
According to NVIDIA, NeRFs and Gaussian splatting can improve reality capture by generating photorealistic 3D scenes and enabling efficient rendering, reducing the time and cost of digitizing spaces.
What this means for businesses: Faster digital twins for training, sales, inspection, and layout planning without time-consuming manual 3D modeling.
How to Implement Photorealistic World Capture Pipelines for AR
There are 3 key steps to take:
- Define a capture standard (coverage, lighting, quality assurance)
- Create a pipeline (capture → reconstruction → optimization → streaming)
- Plan for limitations (asset size, LOD, offline mode, device performance).
Trend #4: Interoperability via Open Standards (OpenXR + OpenUSD)
According to Khronos, OpenXR is a royalty-free open standard that provides a set of common APIs for a variety of AR and VR devices, reducing the cost of reprogramming across different ecosystems.
What this means for businesses: Less vendor lock-in, more portable XR roadmaps, and easier strategies for supporting multiple devices.
How to Implement Interoperability via Open Standards
- Use OpenXR for the runtime interface
- Maintain a feature matrix (no device-specific logic)
- Leverage a unified 3D exchange backbone (OpenUSD, where appropriate) to ensure content portability.
Trend #5: Privacy, Security, and “Bystander Trust” Are Becoming Product Requirements for Glasses
According to The Verge, Meta AI is always enabled on Ray-Ban Meta glasses unless users disable “Hey Meta,” and Meta has removed the option to prevent voice recordings from being stored in the cloud, increasing privacy concerns with wearable cameras.
What this means for businesses: Any AR product that uses cameras/microphones must offer privacy UX, policies, and compliance as core features, or adoption in the workplace and public institutions will stall.
How to Implement Privacy and Security in AR Glasses
There are 5 key steps to take:
- Design clear recording/AI states (visible indicators + easy off function)
- Minimize data collection
- Establish retention/deletion rules
- Offer a “no-cloud/enterprise mode”
- Publish workplace usage policies with training
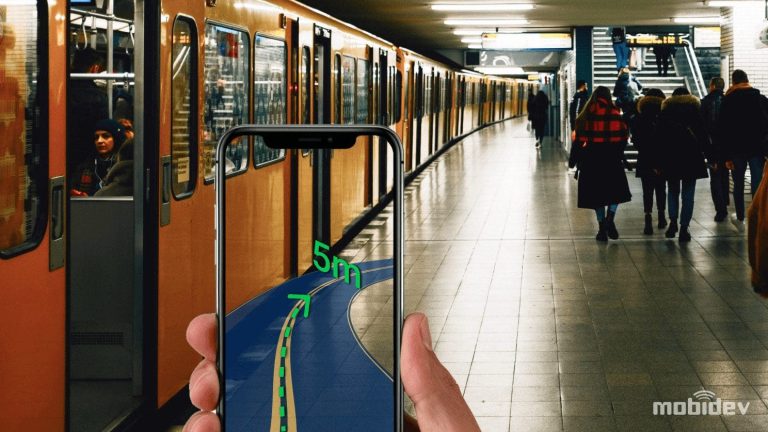
Trend #6: AR Navigation + “AI Maps” and Persistent Spatial Understanding (Shared Anchors at Scale)
A two-dimensional map isn’t the ideal way for humans to navigate. To get a bit closer to something your body is more instinctively comfortable with, you have to try something else. Enter AR navigation. Instead of looking down at a 2D map, 3D directions appear on your mobile phone screen or even a head-mounted display.
The concept is simple, and in many cases, it is achievable, but it comes at the cost of a lot of nuance. No one method of achieving AR navigation works in every situation.
Indoor Navigation Powered by AR
Augmented reality indoor navigation is certainly achievable, but it continues to be limited by several constraints. Precision is the most critical issue. Although indoor navigation systems, when properly implemented, can be quite accurate in terms of helping the user find their way from one department or aisle to another, they’re not precise enough to help them find a specific item on a shelf.
These are the three possible approaches for implementing indoor navigation powered by AR:
- Radio-based: powered by BLE Beacons, Wi-Fi RTT, or ultra-wideband (UWB) ranging
- Markers: visual markers identified by a device with an AR framework
- VPS (visual positioning system): estimating the location using a pre-trained AI model and an image from the camera
Our team at MobiDev demonstrated AR indoor navigation with visual markers at a corporate campus with an ARKit device. Marker-based AR indoor navigation is cheaper to implement than beacons and allows better accuracy, but may be subject to problems like obstruction of markers or misconfiguration. However, the choice of the best approach heavily depends on the specifics of your project.
Outdoor AR Navigation
With a clear view of the sky, more options are available to ensure high-accuracy and precision positioning and navigation. However, GPS isn’t the only technology that can be effective in this space. In situations where GPS isn’t as effective, for example, beneath tall city buildings, other technologies can help fill in the gaps. These might be beacons (for relatively small outdoor locations) or visual positioning systems (VPS).
Google and Apple have both continued to advance their VPS systems in their respective mapping APIs for AR platforms. However, visibility conditions can vary, meaning that these systems may not work as expected in foggy or rainy conditions.
“AI Maps” and Persistent Spatial Understanding (Shared Anchors at Scale)
According to Niantic, a Large Geospatial Model will use large-scale machine learning to understand a scene and connect it to millions of other scenes globally — enabling place-anchored AR at scale.
What this means for businesses: AR shifts from one-off sessions to persistent, location-aware experiences (navigation, guidance, shared context) that accumulate value over time.
How to Implement AR Navigation
There are 4 key steps to take:
- Pick use cases that benefit from persistence
- Implement shared anchors and add sync
- Measure localization confidence with fallbacks
- Formalize consent/privacy around scanning and storing spatial data.
Trend #7: Augmented Reality in Manufacturing + Enterprise-Ready Spatial Devices
Manufacturing is arguably the strongest sector for AR utility, moving beyond “cool demos” to measurable ROI. The value proposition is clear across four key operations:
- Training: New hires can simulate dangerous tasks safely. Instead of reading a manual, they practice on a “digital twin,” allowing them to fail without breaking expensive machinery.
- Maintenance: This is X-ray vision for technicians. AR overlays internal schematics onto the machine or allows a remote expert to draw 3D annotations directly in the worker’s field of view.
- Quality Control: Visual inspection becomes objective. By overlaying the CAD model onto the physical part, deviations or missing components are highlighted instantly.
- Safety: HMDs can visualize invisible hazards, drawing geofenced “danger zones” around active machinery or displaying lockout/tagout status just by looking at the equipment.
For now, the deployment reality is harsh. The shop floor is not a sterile lab, and standard consumer UX fails here immediately. You have to solve the “Glove and Noise” problem. You’ll need to answer a number of questions, such as:
- How does a technician use a touchscreen or precise hand tracking while wearing heavy safety gloves?
- How does a voice command work next to a 90-decibel CNC machine?
If the interaction fights the worker, the device stays in the locker. Adoption fails, not because the data isn’t useful, but because the interface is annoying.
The solution isn’t to force-fit consumer gestures into industry; it is to design for the environment. If hands are busy or gloved, the UI must adapt. Passive interaction is the answer. A good example would be using eye-tracking (gaze dwell) to pull up information simply by looking at a sensor, eliminating the need for taps or voice commands entirely.
Enterprise-Ready Spatial Devices: Entitlements, Sensor Access, and Platform Control
According to Apple’s visionOS documentation, enterprise APIs can grant enhanced sensor access and increased platform control by using entitlements, making governance a first-class requirement.
What this means for businesses: Pilots turn into IT-managed products — permissions, auditing, distribution, and data protection determine whether XR can scale.
How to Implement Enterprise-Ready Spatial Devices
There are key steps:
- Define a role-based access model
- Build an “enterprise gate” (entitlements, audits, policy enforcement)
- Plan private distribution
- Add content protection controls (classification, export limits, watermarking where needed).
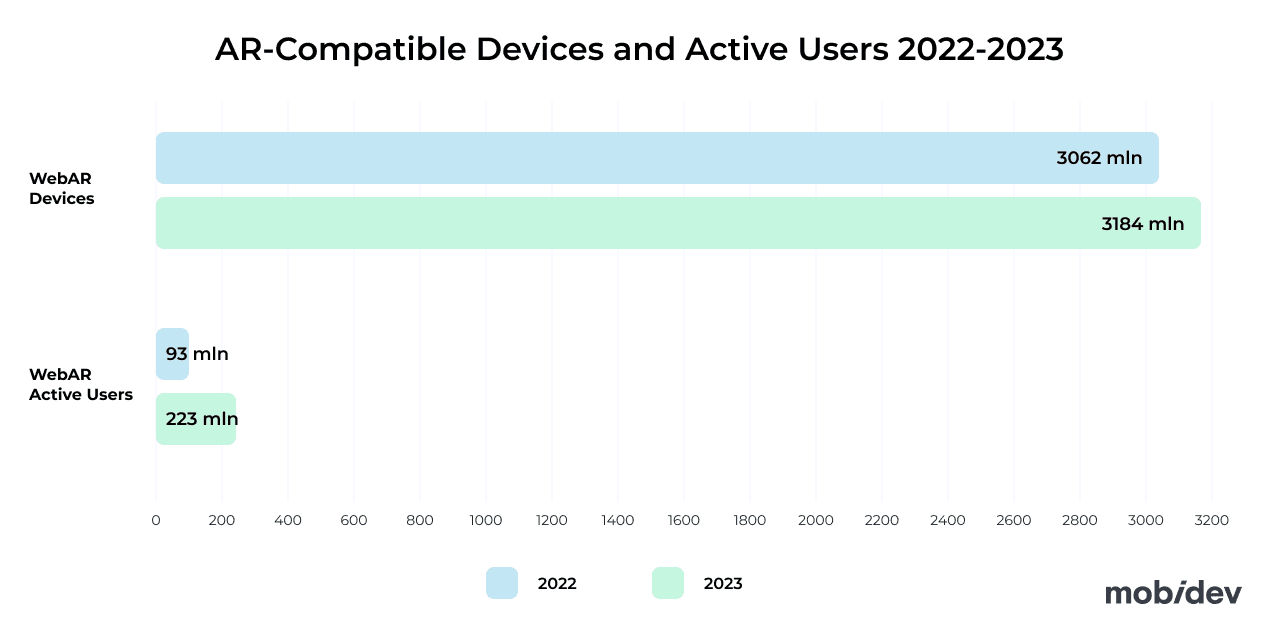
Trend #8: WebAR Helps Build More Accessible Experiences
The differences in mobile AR hardware mean that it can be challenging to create augmented reality experiences that can be used on all devices. WebAR can help level the playing field so long as developers are willing to sacrifice ambitions for innovative AR features.
WebAR may lack the powerful functionality of native AR applications, but it makes up for this with its accessibility. Mobile devices and even desktops with webcams can run basic WebAR experiences. More importantly, users don’t need to install an app. All they have to do is visit the webpage through a link or via a QR code.
WebAR experiences are still the best for simple tasks, like marketing demos, basic virtual try-on, product demonstrations, and other simple tasks. However, more complex games, high-fidelity projects, and other applications that need more power are better suited as native mobile apps.
Learn More: Web Accessibility Testing Explained for Product Owners
Trend #9: Augmented Reality in Marketing
According to Snapchat, marketing campaigns that included AR had 2.4x Ad Awareness lift, 1.8x Brand Awareness lift, and 1.4x Brand Association lift compared to similar campaigns without AR.
There are many ways to utilize augmented reality in your marketing campaigns. Here are 3 popular ideas:
- Business cards: Create a QR code and add it to your business card. When people scan it with their smartphones, a webpage with a WebAR experience opens. It demonstrates your company’s expertise. Check how such a solution works here.
- User manuals: Create an interactive AR user guide for appliances like coffee makers. See our case study as an example.
- Product demonstrations: Create virtual fitting rooms, furniture, or equipment in AR. The sky is the limit for AR product demos.
Case Study: AR Marketing Campaign
Our team at MobiDev collaborated with a travel company to create an AR-based application for marketing purposes. In addition to contextual information from points of interest in the camera view, the app can also provide ticket booking functionality. This allowed the client to gain a lot of media attention, strengthen the brand, and turn it into new business opportunities.
Trend #10: Augmented Reality in Healthcare
With head-mounted displays, the door of possibility opens for hands-free interfaces. There is demand for augmented reality in the healthcare sector for several applications, such as:
- Surgical aid: Hands-free overlays for surgeons with real-time data and organ models can help enhance surgical procedures.
- Training: Medical students can simulate complex surgeries with 3D anatomical models without cadavers.
- Vein visualization: HMDs can help display vein outlines on patients’ skin, making IV insertion less painful for patients.
- Therapy and rehabilitation: AR experiences can enhance physical therapy regimens, and AR can be used for certain forms of therapy, like exposure therapy for PTSD patients.
Google’s Augmented Reality Microscope (ARM) demonstrates that augmented reality and machine learning technologies can be used to display digital overlays in an optical microscope to enhance cancer detection and classification for medical professionals. Although the project is open source, models are only available on request. The project demonstrates that augmented reality has enormous potential as an aid in disease detection.
Read More: Augmented and Virtual Reality in Healthcare: Use Cases, Challenges, & Opportunities
Trend #11: Augmented Reality in Retail and eCommerce
Augmented reality was, at one point, a novel, experimental, and unfamiliar technology for retail software development. However, virtual fitting room applications have become widespread, with brands adopting them directly in their flagship shopping applications as a feature.
Physical stores can also benefit from this technology by installing smart mirrors at showrooms, enabling customers to visualize how various items will look on them without the need for a fitting room. This exemplifies effective smart design in business.
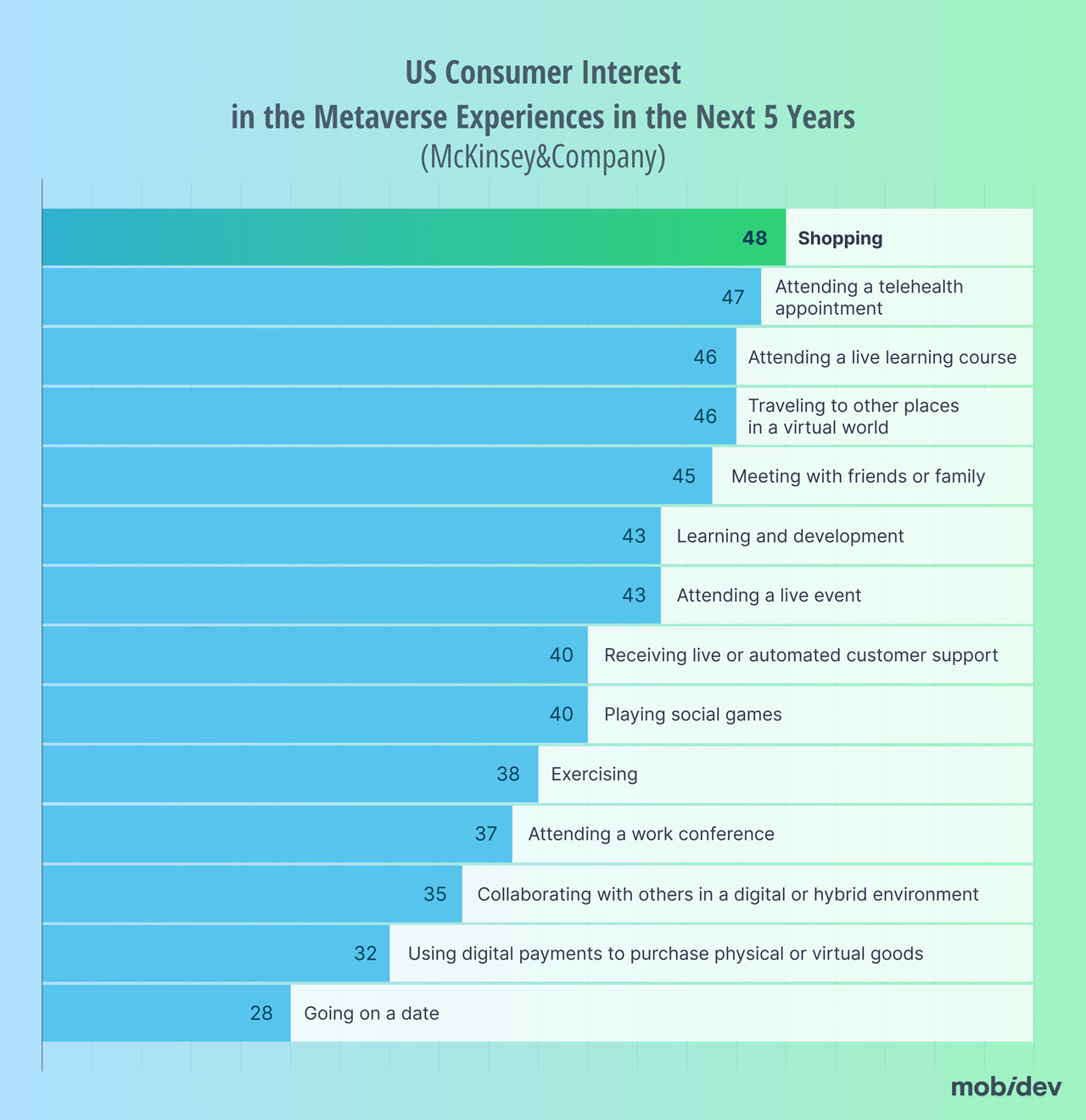
Although the hype and novelty of these applications have worn off, virtual try-on is now a critical part of the e-commerce experience for shoppers. A few years ago, a McKinsey & Company survey revealed that 48% of consumers were most interested in augmented reality shopping in the next five years. That interest has been realized thanks to AR shopping features provided by retailers like Ikea, Target, and more.
Shopping was the most interesting metaverse application for 48% of responses.
They aren’t the only ones. GlobalData reports that the retail industry has seen over 59,000 patents filed and granted over the past three years, with virtual try-ons highlighted as a key innovation area in VR/AR. To keep up with the competition, retailers should evaluate where AR virtual try-on can add the most value for customers.
Read about Augmented Reality in Retail, Use Cases, Challenges, and Best Practices for Leveraging in SaaS
Trend #12: Augmented Reality in the Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is incorporating several technologies mentioned earlier in this piece. Check out these 4 use cases of AR in the automotive industry:
- Sales: AR experiences are being used to help sell cars, where users can see virtual cars in a real-world environment via mobile apps
- Remote assistance: Providing guided assistance and troubleshooting for drivers
- Parking spot detection: Highlighting empty parking spots in busy garages. Tesla has incorporated this into their car displays when selecting spots to park in using AI.
- Detecting driver drowsiness: Detect drowsy behaviors from drivers and alert them before they fall asleep.
Heads-Up Displays in Cars
Distance Technologies is developing a 3D heads-up display for cars. With full color, the prototype demonstrates how drivers could benefit from seeing non-intrusive information about their driving displayed on their windshield. Some of these features include a speedometer, 3D visualizations, phone calls, as well as voice and gesture controls. The prototype requires more development, such as increased brightness, but it is still an impressive look into the future of what’s to come for the automotive industry.
Trend #13: The State of the Metaverse and Social AR
Social AR is still in demand for some consumers, but we’ve clearly entered the trough of disillusionment for the metaverse. Instead of chasing a single, fully interconnected virtual world, brands are focusing on more grounded social AR experiences that people can actually adopt and return to.
In other words, the “metaverse” narrative cooled down, but the underlying social layers didn’t disappear — shared presence, identity, and lightweight co-experiences are still moving forward, just in more practical forms.
Learn How to Build an AI Assistant: Virtual Assistant Technology Guide
Codec Avatars and Realistic Social Presence
For example, Meta has an open-source technology called Codec Avatars that is designed to help people interact in a digital environment. Since the technology is open source, it could theoretically be utilized on any headset given sufficient integration. Importantly, realistic avatars and face-scanning technologies are increasingly empowered by advancing AI capabilities, which help social interaction feel more natural and expressive.
What This Means for Businesses
For businesses, the opportunity is less about “building a metaverse” and more about adding social value where it matters. Think about live events, community, collaborative shopping, shared learning, and remote support. The teams that win here typically focus on clear use cases, measurable outcomes, and trust fundamentals (identity, moderation, and privacy) rather than trying to recreate the entire internet in 3D.
Recent Augmented Reality Trends That Have Become Must-Have
We’ve been tracking AR trends for a while, and some technologies that were deemed trendy in previous years have become mainstream and even must-haves. In this section, we share the trends of previous years that have transitioned from nice-to-have.
Trend #1: Mobile AR (Platform Updates + Connectivity)
Mobile devices remain the dominant platform for augmented reality applications among users. This applies not only to consumers, but to business use cases as well. Businesses utilize mobile AR for products like remote assistance, training, product visualization, and other applications.
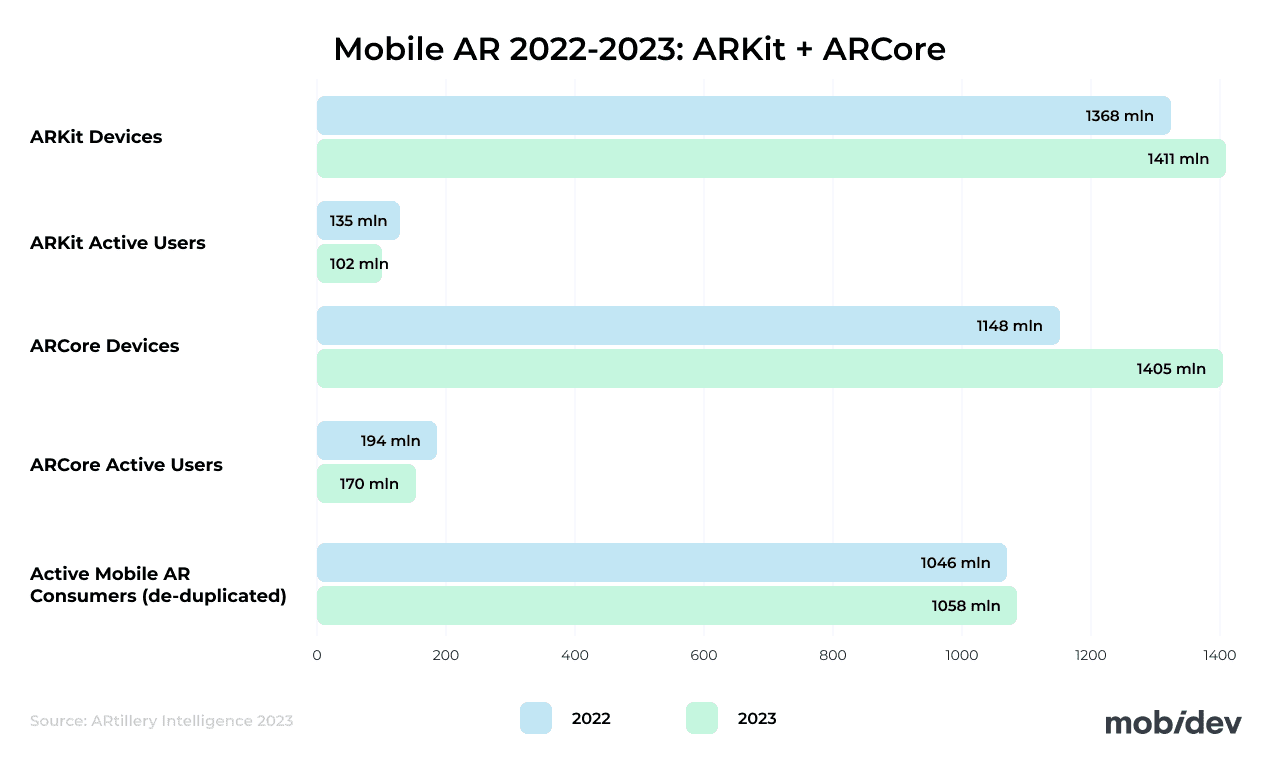
According to Statista, the number of active mobile AR devices is continuing to rise, with projections of 1.19B mobile AR users worldwide by 2028.
ARCore 1.51.0 (The Release That Mattered for Many Teams)
ARCore, Google’s augmented reality software development kit for Android devices, has seen a few iterative updates since last year. The latest version is 1.51.0, which includes ongoing refinements and fixes. Separately, ARCore’s Flash Mode (torch) support enables higher-quality AR experiences in dark environments.
At the same time, v1.48.0 was more impactful for many teams because it added support for Unity 6 and AR Foundation 6 — an important stack for Unity-based AR apps.
In 2024, ARCore 1.43.0 enabled the Places API in Geospatial Creator migration. The Places API is a component of Google Maps used to extract useful information about place names, addresses, and categories for use in AR applications. So, if a user points their camera at a landmark, the Places API can supply your application with the information it needs to overlay contextual information about the landmark.
There have also been a few other iterative releases, bug fixes, and other improvements to ARCore that have happened over the past year.
ARKit (Stable Feature Set, but an Important Framework Shift)
ARKit has also seen a few iterative updates recently, but ARKit 6 is still a key baseline version. There isn’t much word about what ARKit 7 might entail.
ARKit 6, which was released in October of 2023, enables developers to utilize several new features, such as:
- 4K Video: Capture high-resolution videos of AR experiences for professional video editing and social media apps.
- Location Anchors: New location anchors for AR experiences include Montreal, Sydney, Singapore, and Tokyo.
- Instant AR Placement: LiDAR scanner enables quick and seamless placement of AR objects without a lengthy scanning process.
- Enhanced Motion Capture: Human pose estimation algorithms can enable motion capture experiences.
- Scene Geometry: Object occlusion and real-world physics for virtual objects are made possible with a topological map of the scanned scene. With RoomPlan, users can quickly create floor plans of structures as well. This is critical for AR measurement applications.
- Simultaneous Front and Back Camera: It’s possible that users can control content seen with the rear camera by moving their face.
In June 2024, Apple improved ARKit with the ability to detect objects in the real world and attach content to those objects with the ObjectTrackingProvider. This is a component of ARKit that helps the device track real-world objects using references. Developers can set the parameters for how these capabilities should behave as well. In addition, the June update allows applications to utilize the RoomTracking Provider to understand the shape and size of the room that people are in and detect when the device has moved to another room.
This being said, Apple has deprecated legacy approaches that were commonly used in 3D/AR pipelines (like SceneKit) and increasingly pushes modern spatial rendering work toward RealityKit where it fits. That shift affects long-term tech choices even when ARKit itself isn’t “dramatically new.”
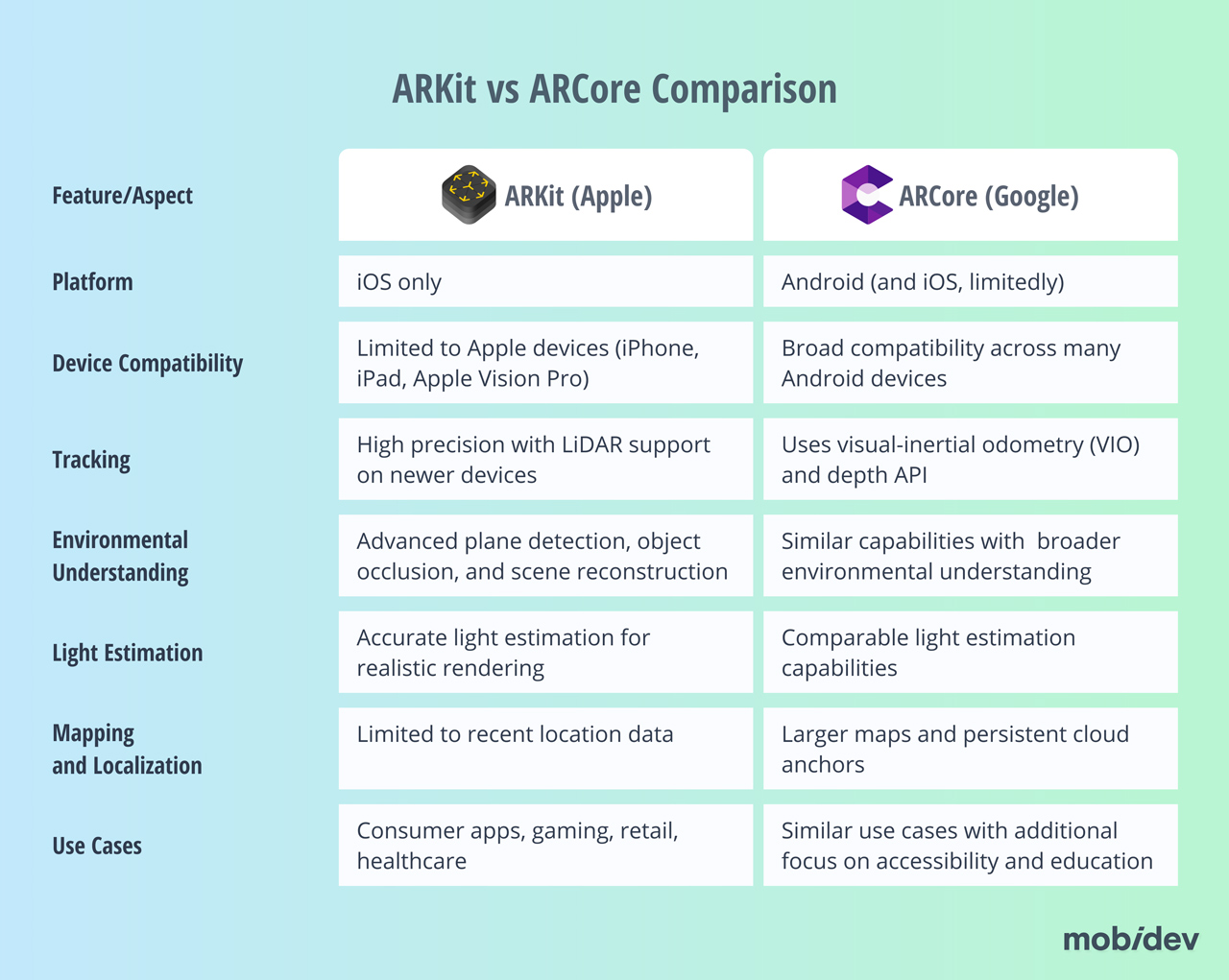
ARCore vs. ARKit
Since not much has changed in either framework, not much has changed since last year when it comes to comparing the two frameworks against each other. Both are comparable SDKs that work well with their ecosystem. Neither exceeds the capabilities of the other in any category.
You should also consider that not all devices support the hardware needed for many of the more powerful features of each platform. For example, many of the most advanced ARKit features require the iPhone LiDAR scanner. The LiDAR scanner is only present on the Pro and Pro Max variants of the iPhone. This has been the trend since the release of the iPhone 12 Pro and Pro Max in 2020 and has continued with the iPhone 17 Pro and Pro Max.
Read Lidar App Development Guide: Practical Experience and Knowledge Base
Similarly, the hardware differences across many Android phones mean that the most powerful ARCore features can only be used on some newer, high-end devices. That means you may need to consider that not all users will have the same experience with your ARCore application.
5G Connectivity and Mobile AR
Augmented reality is a powerful technology, but it can be limited by connectivity. If your experience depends on a cloud server for map data, 3D models, and other processing, then a strong Internet connection is needed. This means that many experiences have been limited to strong Wi-Fi networks in the past. However, 5G connectivity has improved significantly over the past few years.
This means that developers have more freedom to create AR experiences that users may find more helpful outside of their own homes. This may apply to outdoor AR-based navigation experiences and tourism applications with AR informational pop-ups.
Cross-Platform AR Applications Continue to Evolve
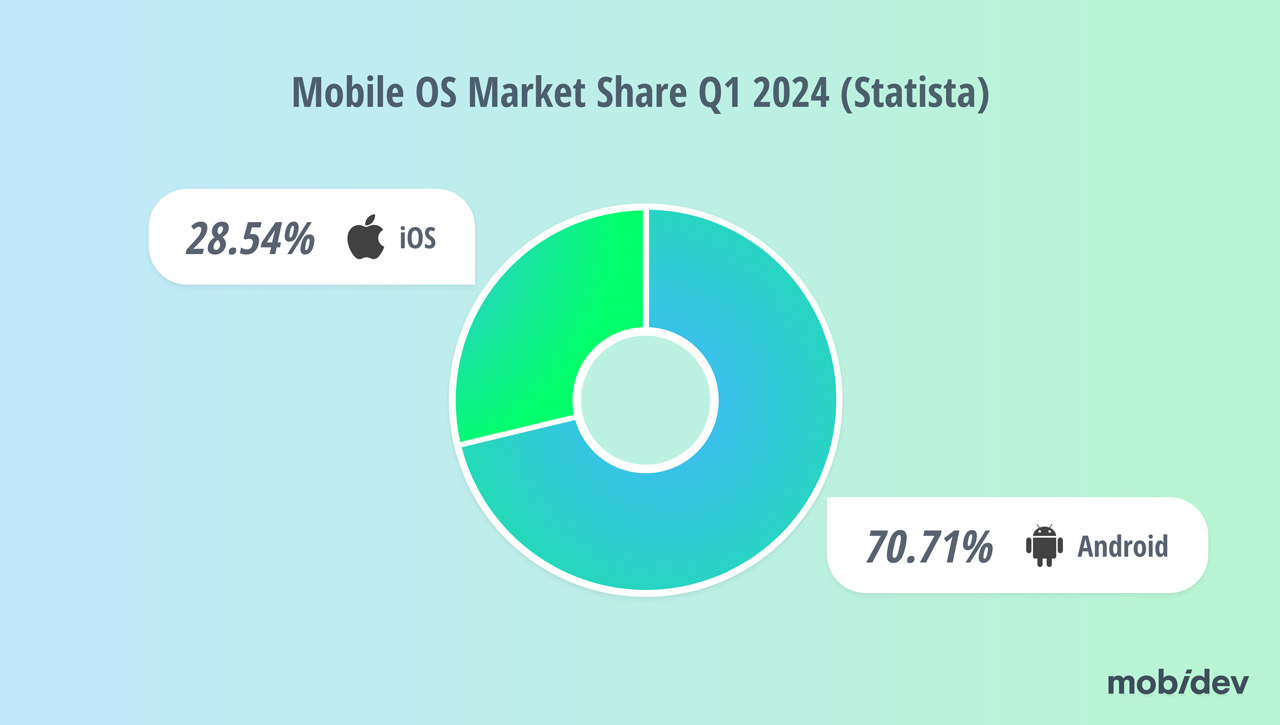
Most AR-capable smartphones are Android devices, with 70.36% of the mobile OS market share in Q1 2026 belonging to Android, according to StatCounter (a slight drop from 70.71% in Q1 2024).
However, despite this gap, there are still great strategic reasons why you would want to target both audiences. For one, a cross-platform app experience will enable you to reach a much wider audience than just Android users. What may be more important are demographics. iOS users are a higher-spending customer base. It also depends on what market you’re targeting. For example, iOS has a strong market presence in the United States.
Cross-platform applications may allow you to reach a wider audience, but you should remember that they still have more limited capabilities. If your app isn’t that complicated, or if you’re offering a simpler AR experience, a cross-platform application may be perfect for you. If you need to offer high-fidelity features and need more power, it’s worth considering creating two separate native applications, one for Android and one for iOS.
Learn How to Create an Augmented Reality App: Business Owner’s Guide
Trend #2: Wearable AR Experiences Get More Common (Vision Pro + Quest + Galaxy XR )
It’s been over two years since the Apple Vision Pro launched, and while it hasn’t exactly gone mainstream yet — estimates from the Financial Times put 2024 shipments around 390,000 units — it’s clearly more than just an expensive prototype. Apple is addressing early feedback with iterative refinements: the M5 chip brings a meaningful performance uplift, while the Dual Knit Band targets comfort improvements. It’s not a complete redesign, but it’s a refresh that helps the platform stay relevant heading into 2026.
Thankfully, developing for the Vision Pro doesn’t depart too far from mobile AR development for iPhones. The Vision Pro utilizes the visionOS SDK, allowing developers to use familiar Apple tools such as SwiftUI, RealityKit, and ARKit. Existing applications can also be adjusted to work well with visionOS.
Read about Apple Vision Pro App Development, Business Opportunities and Strategies
Meta Quest Devices
Meanwhile, Meta continues to dominate the consumer side. They’ve fleshed out their lineup with the powerful Meta Quest 3 and the budget-friendly Meta Quest 3S, strengthening their position in the market. Both headsets run on Meta Horizon OS (still built on AOSP, making it familiar territory for Android devs) and bring high-quality color passthrough to a mass audience. This allows users to blend digital screens with their physical surroundings more seamlessly.
There are also several immersive AR applications, such as:
- PianoVision: learn to play the piano in augmented reality using hand tracking
- Demeo: a dungeon crawler mixed reality game where you can see the game board in AR
- Movies and TV: watch video content in AR windows on your headset
Many people online write that they’re disappointed in how few mixed-reality applications there are for the Quest lineup. However, the few that do exist demonstrate that these apps are possible to create. As a result, mixed reality games for the Quest 3 and Quest 3S (along with the existing Quest Pro installed base) are an opportunity for app developers to meet that demand.
Recently, Samsung presented the Galaxy XR headset, which is similar to Apple Vision Pro, but is implemented on the basis of Google’s Android XR. This is the first product built on this platform, the result of cooperation between Qualcomm, Google, and Samsung.
Make the Most Out of AR Trends with MobiDev
All augmented reality trends look exciting, but just because a technology is trending doesn’t mean that it will be the most effective solution for your business. You need to explore these trends to find the technologies that will work best for you and help you meet your business goals. Not only that, but you need to see if implementing that technology is feasible and meets market needs. So, how can you decide if starting that work is right for your brand?
The best way to get started is to talk to experienced augmented reality consultants. With over 15 years in software development, our team is prepared to take care of your product from concept to launch.
FAQ
AR overlays digital content onto the real world, typically without deeply understanding or interacting with physical geometry. MR usually implies stronger spatial understanding (meshing, occlusion, anchoring) so digital objects can “behave” like they’re in the real space and interact with it more naturally. In practice, the terms overlap in marketing—what matters is whether your experience needs persistent, spatially aware interactions (MR-like) or simple overlays (AR-like).