Contents:
Until we can learn to turn back time, healthcare systems will continue to age. Patient needs are increasing, and diseases continue to evolve. As the scale of challenge grows for healthcare industries around the world, inefficiency isn’t affordable anymore. If you’re a healthcare provider, innovation is critical to stay afloat in a competitive market. Augmented and virtual reality technologies can help you achieve this goal.
In what follows, we’ll explore real-world examples of how AR and VR are helping healthcare organizations innovate affordably. We’ll also share MobiDev’s experience in this field and practical advice on incorporating AR/VR into healthcare.
How Augmented Reality is Used in Healthcare: Benefits & Applications
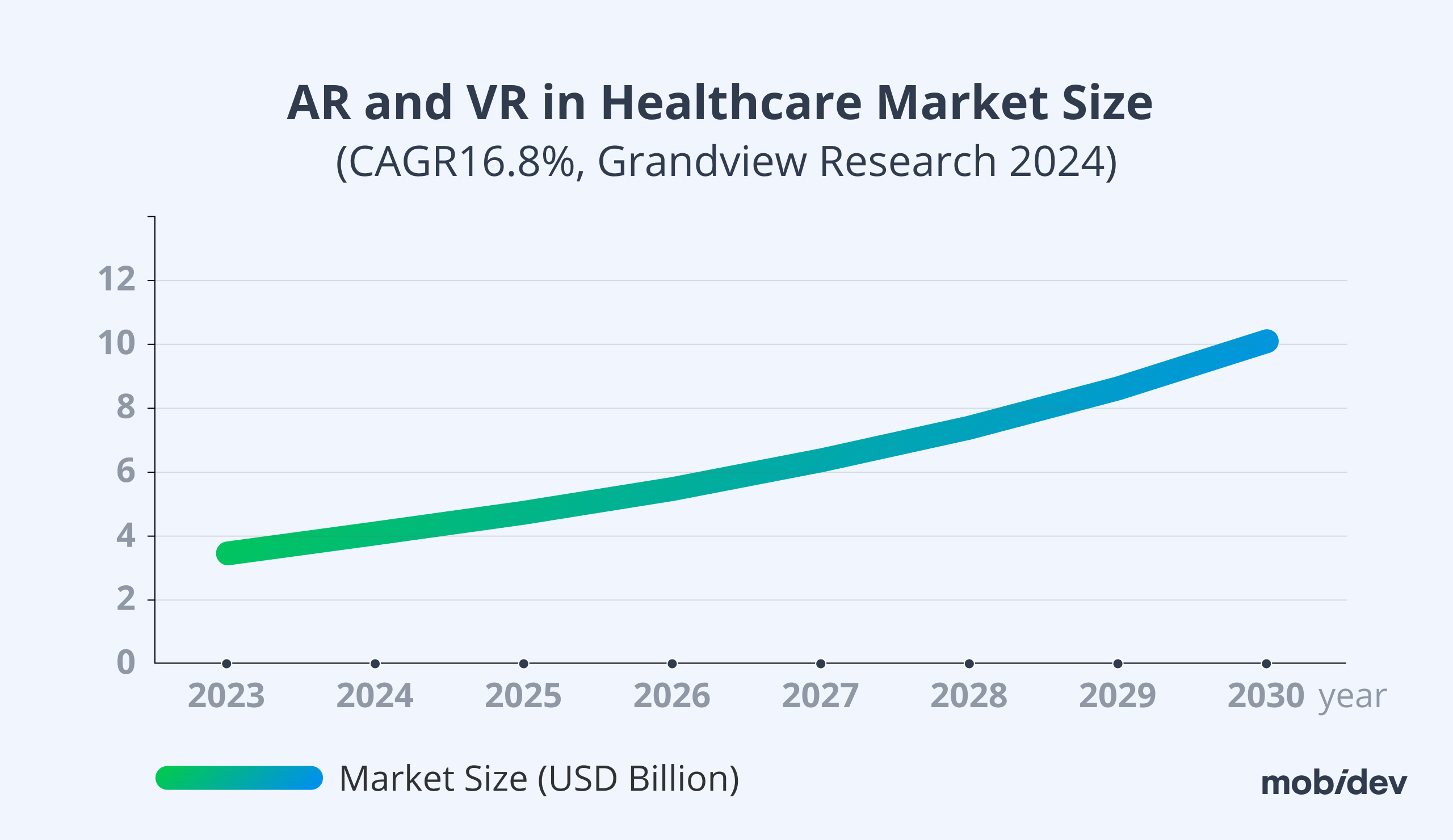
According to Grandview Research, the market size of augmented and virtual reality technologies in the healthcare industry will be worth over $10 billion by 2030. This growth is due to the advancing availability of telemedicine, the improved abilities of VR and AR technologies to aid surgery processes and training, use in mental health treatments, and medical education. Augmented reality and virtual reality offer immersive experiences for their users. Although there are obvious benefits for the entertainment industry, many opportunities emerge for healthcare applications. We can look at these benefits in two categories:
- Professional: AR and VR for medical practitioners; training, support, and disease research are some examples
- Patient: telehealth, therapy, education, and personal health and wellness
Let’s look at some more specific use cases of AR and VR in the healthcare industry.
1. AR/VR in Medical Training and Education
Traditional medical training methods often struggle to keep pace with rapid advancements, creating a gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. AR and VR address this issue by providing immersive, hands-on experiences that bridge classroom learning and clinical practice. Through surgical simulations, emergency scenarios, patient care exercises, and rehabilitation training, medical professionals can refine their skills in a controlled environment, reducing the risk of human error.
Several applications demonstrate the transformative impact of AR and VR in medical training. Some notable examples include SimX, FundamentalVR, Osso VR, Augmedics, HoloAnatomy by Microsoft, Health Scholars, and Laboratory VR Training Simulation, offering innovative solutions with detailed visualization, training analytics, and scenario editing.
These platforms incorporate essential components like visualization and simulation systems to create comprehensive training modules. The tech stack involves sophisticated hardware and advanced audio-visual technologies. By making medical training more engaging and effective, VR benefits medical schools and practitioners while presenting a lucrative opportunity for startups to improve their revenue cycle.
2. Augmented Reality Diagnostics
Identifying and understanding diseases and conditions can be made much more efficient and seamless when paired with augmented reality technologies. Google’s AR microscope project enables oncologists to detect cancer. By using AI to identify cancer cell candidates, the system can visually highlight the areas of view in the microscope for the user to see.
Another example is 3D imaging. AR can display 3D images from MRI, CT scans, or X-rays directly onto a patient’s body. This allows healthcare professionals to visualize complex anatomical structures in real-time, improving accuracy during diagnostics. In the same way, AR can help nurses locate veins for blood drawing or IV placements. This can increase the success rate of these procedures.
3. Augmented Reality for Hospital Navigation
Hospitals can be vast, and it’s easy to get lost in them. Traditional maps can help, but they can be difficult to use when confronted by multiple floors and the experience can be disjointed as you look up and down between your map and the real world. Augmented reality-powered indoor navigation for hospitals can help bridge that gap by presenting immersive directions in 3D on a mobile device. MobiDev has tested this technology for a corporate campus, and these same techniques can be applied to hospitals as well.
Researchers have evaluated AR-based indoor navigation systems for hospitals before. A study from the Bern University of Applied Sciences found that 8 out of 12 participants in their study preferred to use their AR-navigation app in the hospital. However, there were some challenges; some participants reported fatigue from constantly holding their phone in front of their eyes.
4. Augmented Reality in Surgery
Doctors are benefitting from augmented reality’s ability to enhance surgeries. In June 2020, John Hopkins neurosurgeons performed augmented reality surgery on living patients for the first time, including spinal fusion and tumor removal. By utilizing a head-mounted display, surgeons could see projected images of patient anatomy.
However, there are some challenges. Human bodies are highly dynamic. Real-time adjustments are needed for AR systems to account for these changes. Maintaining accurate projections in AR experiences is crucial for surgeons to prevent mistakes and ensure successful outcomes.
5. Augmented Reality for Mental Health Care
AR and VR are increasingly being integrated into therapeutic settings. These technologies are applied in exposure therapy to help patients confront and manage their phobias, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and anxiety disorders in a controlled environment. By recreating situations that trigger anxiety or fear, AR and VR allow patients to face their challenges safely and systematically, under the guidance of a therapist. This immersive approach not only enhances traditional therapeutic methods but also engages patients more deeply, making treatments more effective and impactful.
AR and VR can make mental health treatments more accessible by offering remote therapy options for patients who may not have easy access to in-person therapy. Additionally, ongoing research highlights the future potential of AR and VR in mental health care, suggesting that these technologies could transform the field by providing more personalized and efficient mental health support.
6. Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality in Telehealth
Immersive technologies like AR and VR are enhancing telehealth by providing patients with interactive ways to understand their medical conditions, making treatments more transparent and less intimidating. They also improve access to specialized care for remote patients and offer realistic training environments for healthcare professionals, expanding the reach and effectiveness of healthcare services.
Communication
AR offers 3D visualizations of medical conditions, treatments, and anatomy directly in the patient’s environment. This innovation allows patients to gain a clearer understanding of complex medical information and procedures, enhancing the effectiveness of discussions with their doctors.
During telemedicine consultations, doctors can utilize AR to create interactive experiences where patients engage with virtual models or simulations, clarifying their conditions and treatment options. Additionally, AR enables both doctor and patient to view the same content simultaneously, fostering collaborative discussions about treatment plans and encouraging patient involvement in decision-making processes.
Symptom Detection
New possibilities emerge for self-diagnosis and symptom identification thanks to AR technologies. Patients can use AR apps on their smartphones to scan their bodies, with the app overlaying information about potential symptoms based on visual input, which helps users identify issues like skin conditions or swelling.
This technology empowers patients by guiding them through self-examination techniques, such as checking for lumps or irregularities, and by providing step-by-step visual instructions and highlighting areas of concern. Moreover, AR apps serve as awareness tools, educating patients about common symptoms associated with various diseases, aiding them in recognizing warning signs, and seeking timely medical attention.
Instructions & Manuals
Patients can use AR applications to help them understand how to use medical devices at home. 3D instructions can be displayed on mobile devices to help them follow protocols more accurately while communicating with their doctor. For example, an at-home blood test could be accompanied by an AR instruction manual to help patients understand how to use each of the kit’s pieces.
7. Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation with AR and VR
AR and VR can be highly beneficial for patients requiring physical therapy and rehabilitation. One strength of extended reality is enhancing patient engagement and motivation. By incorporating gamification into therapy sessions, AR and VR transform potentially monotonous exercises into interactive and enjoyable activities. This not only makes the therapy process more appealing but also encourages patients to adhere to their treatment plans.
Additionally, AR applications can provide real-time feedback on exercise execution, allowing patients to immediately correct their movements. This instant feedback loop ensures that exercises are performed correctly, reducing the risk of injury, and improving overall treatment outcomes.
AR and VR applications can be adapted based on individual progress and specific requirements, ensuring that therapy is both efficient and effective. Moreover, extended reality can simulate real-life scenarios, enabling patients to practice daily activities within a controlled and safe environment. This aspect of immersive experiences is particularly beneficial for boosting patients’ confidence and preparing them for the challenges they may face post-recovery. By integrating these innovative elements, AR and VR significantly enhance the physical therapy and rehabilitation experience, leading to more successful and satisfying patient outcomes.
As an example, XRHealth has several FDA-registered VR applications that enable physical therapy patients to complete their routines in a fun and engaging way.
File name: physical-therapy-rehabilitation-with-virtual-reality
Alt/title: AR and VR significantly enhance the physical therapy and rehabilitation experience
8. Augmented Reality in the Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry benefits from AR in several ways, from drug marketing to psychological care. Pharmaceutical companies leverage AR to create immersive and informative content that enhances patient education, helping patients understand their diseases and treatments better. Through interactive modules, patients can visualize how a drug interacts with the body, fostering a deeper comprehension and adherence to prescribed therapies.
Furthermore, AR’s application in marketing and advertising has proven to be highly effective, as it produces engaging and informative experiences that build trust among consumers. This immersive approach to marketing not only captivates the audience but also significantly boosts sales by providing a thorough and memorable understanding of pharmaceutical products.
AR also enhances quality control by overlaying crucial digital data onto physical products, reducing human error, and ensuring high standards of product quality and patient care.
Use Cases for Virtual Reality in Healthcare
Let’s turn our attention to a few other VR applications in healthcare.
In healthcare, one major application of virtual reality is in pain management and mental healthcare, where it has proven effective in reducing pain and alleviating anxiety. By immersing patients in tranquil virtual environments, it helps distract them from discomfort, providing substantial relief. Moreover, it combats social isolation by enabling virtual social interactions, which can be particularly beneficial for elderly patients and those with limited mobility.
In physical therapy and rehabilitation, VR supports recovery through engaging exercises, making the therapy process more enjoyable and effective.
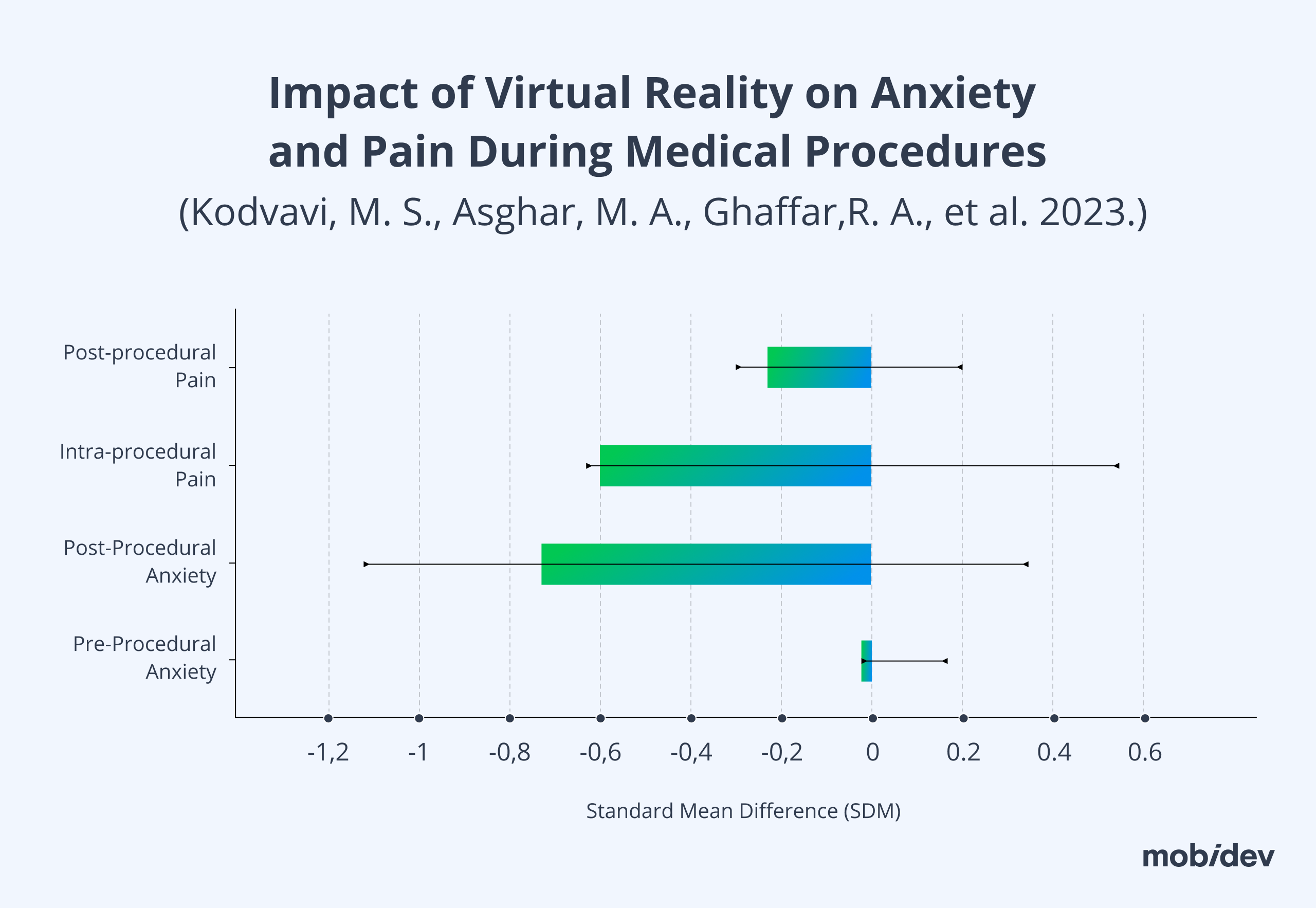
The clinical evidence supporting its efficacy is compelling, with numerous studies showing significant reductions in pain and anxiety levels. The prospects for virtual reality in healthcare are promising, with ongoing research and investment expected to expand its role. It is poised to offer innovative solutions for a variety of medical conditions, further cementing its place in the healthcare landscape.
As an example, in a study by Kodvavi, M. S., Asghar, M. A., Ghaffar, R. A., et al. in 2023, VR was found to be highly beneficial for reducing anxiety and pain after and during procedures. As a result, patients feel more comfortable. However, their study found that VR therapy did not have an impact on easing anxiety prior to procedures.
Top 5 Challenges and Best Practices for Adopting AR/VR in Healthcare
Although AR and VR are promising technologies for the healthcare industry, some challenges must be considered before implementing them. Once you overcome these challenges, you can reap the full benefits of AR and VR and maximize benefits to patients and healthcare professionals. Consulting with AR/VR professionals can help you understand your needs and the best approach to take on these challenges while maximizing your application’s benefits.
Interested in AR Consulting?
Learn more-
Patient Data Protection & Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to patient data protection and regulatory compliance is crucial for AR and VR technologies in healthcare. Regulations like HIPAA in the U.S. set strict standards for safeguarding patient health information (PHI).
AR/VR solutions must ensure data collected, stored, or transmitted complies with these regulations. This protects patient information from breaches and misuse, aligns legal responsibilities, and fosters trust and reliability, which are essential for the successful integration of these technologies in healthcare. This is especially important since VR and AR experiences require environment scanning in most cases to work properly.
-
Data Encryption
If your AR or VR application requires any kind of data to be exchanged between the device and a remote server, it must be properly encrypted to prevent manipulation and exfiltration. You also need to properly encrypt stored data in case a device is externally or physically compromised. This will safeguard you against data breaches.
-
Informed Consent
You must be transparent with your application’s users. Patients and healthcare professionals must be informed about how their data will be used, including any data collected through AR/VR applications. This will also ensure that your application is compliant with legal regulations.
-
Anonymization and De-identification
If you are collecting usage data to improve your product, you will need to ensure that the data is anonymized to de-identify patients. This removes all identifiable information from the data, allowing you to analyze the data without compromising patient privacy.
-
Third-Party Risk Management
If your application involves any third-party vendors, you’ll need to ensure that these vendors also comply with data privacy regulations. Regular audits and assessments can help mitigate risks associated with third-party data handling.
Innovate your Healthcare Business with MobiDev’s AR Consulting & Development Services
With over a decade of experience in the software development market since 2009, MobiDev brings a unique blend of healthcare software expertise and advanced AR capabilities.
Our proven record in ensuring regulatory compliance with standards such as HIPAA and GDPR makes us a trusted software development provider for healthcare organizations all over the world. Whether you need AR consulting or AR development services, MobiDev is committed to meeting your specific needs, ensuring that your AR/VR applications are innovative, secure, and fully compliant.