Contents:
Remaining competitive in your market means constant innovation. Moreover, augmented reality is one of the most cost-effective technologies to apply this strategy. However, one thing I’ve learned during my involvement in AR development since ARKit was first launched in 2017 is that AR projects are often more complex than they appear.
This guide will show you how developing a complex, practical, and innovative AR application works from beginning to end. In what follows, you’ll learn about the technologies used for AR development, how they compare to one another, and the best practices to turn your idea into a market-ready product.
Understanding AR Applications and How They Work
Augmented reality (AR) applications overlay digital information onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception and interaction with their environment. These applications utilize cameras, sensors, and advanced algorithms to recognize and interpret physical surroundings in real-time. By combining these real-world inputs with computer-generated elements such as graphics, sounds, and data, AR creates immersive and interactive experiences that can be applied across various industries.
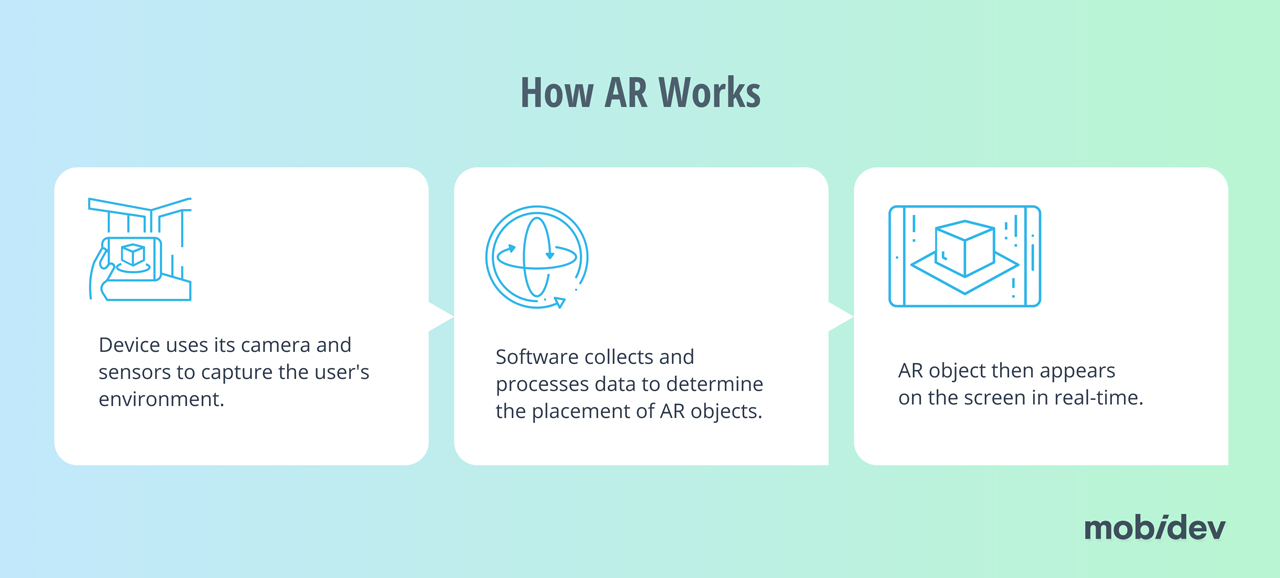
How does AR work:
- Device uses its camera and sensors to capture the user’s environment
- Software collects and processes data to determine the placement of AR objects
- AR object then appears on the screen in real-time
In practical use, AR applications can transform how businesses operate, from streamlining construction projects through virtual blueprints to revolutionizing the retail experience with virtual try-ons and interactive product displays. Education and training also benefit significantly, offering direct learning through simulated environments.
The technology involves a complex interplay of hardware and software, requiring robust development platforms like ARKit, ARCore, and cross-platform solutions to ensure seamless and realistic integration of augmented elements into everyday settings.
Technologies Used to Develop Augmented Reality
There’s more than one way to achieve your vision for your AR application. Let’s briefly look at the various technologies used to develop augmented reality applications and weigh the options.
Target Platforms
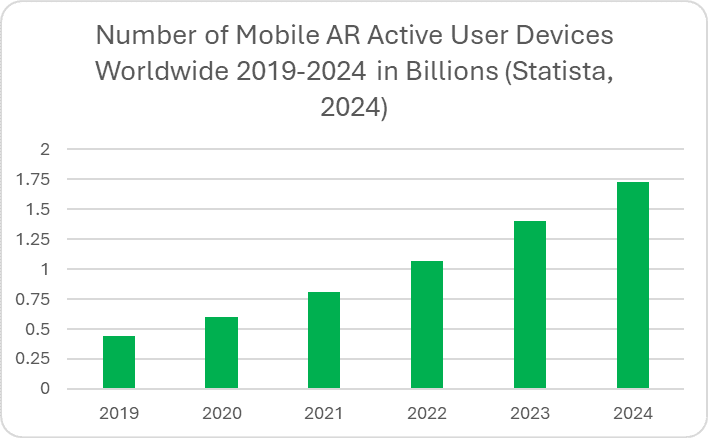
The first question you should ask yourself is: what platform are you targeting? Statista reports that there were nearly 1.75 billion active AR devices worldwide in 2024. The most established and widespread product category is smartphones, meaning that mobile AR makes up the largest slice of the market. However, head-mounted displays like the Apple Vision Pro and Meta Quest lineup are making waves as well.
Mobile AR
Already in the pockets of millions of people and not as bulky or heavy as a headset, mobile AR’s advantage in the market is clear. Its potential for profitability, brand awareness, and user engagement is a demonstrated trend that has solidified the technology’s position in the mainstream in several industries, especially retail.
There are several approaches to mobile AR: native applications that use ARCore and ARKit SDKs, cross-platform applications, and WebAR.
If you’re making a complex project with lots of moving parts and need powerful features, native approaches with ARCore and ARKit are the best options. If you want the app to be available on both Android and iOS, you’ll have to develop two similar apps using both frameworks. Although it can be more difficult and time-consuming, the resulting quality will be higher.
However, if your app is simpler, you might use a cross-platform approach, either through a cross-platform SDK or WebAR. This has the advantage of simplifying the development process down to a single app. Code only has to be written once with a cross-platform application for it to work on your target platforms. However, this comes at the cost of sacrificing powerful features that you’d have with a native AR application.
Native SDKs for AR App Development
ARKit and ARCore SDKs have been in tight competition over the past several years with their native features. Both frameworks recently have introduced powerful location-based features like coordinate anchors to position objects in the real world, creating high-fidelity renders of human faces, placing objects with respect to image depth, measuring distance between two points, and capturing the geometry of real-world environments.
You should consider that not all devices will have the same capabilities. This is especially apparent in Android phones, which have a wide variety of differences in hardware. As a result, some advanced AR features may not be available or work as expected. The same applies for iPhones. For example, only the iPhone 12 Pro and Pro Max models and their successors have LiDAR scanning hardware.
Cross-Platform AR App Development
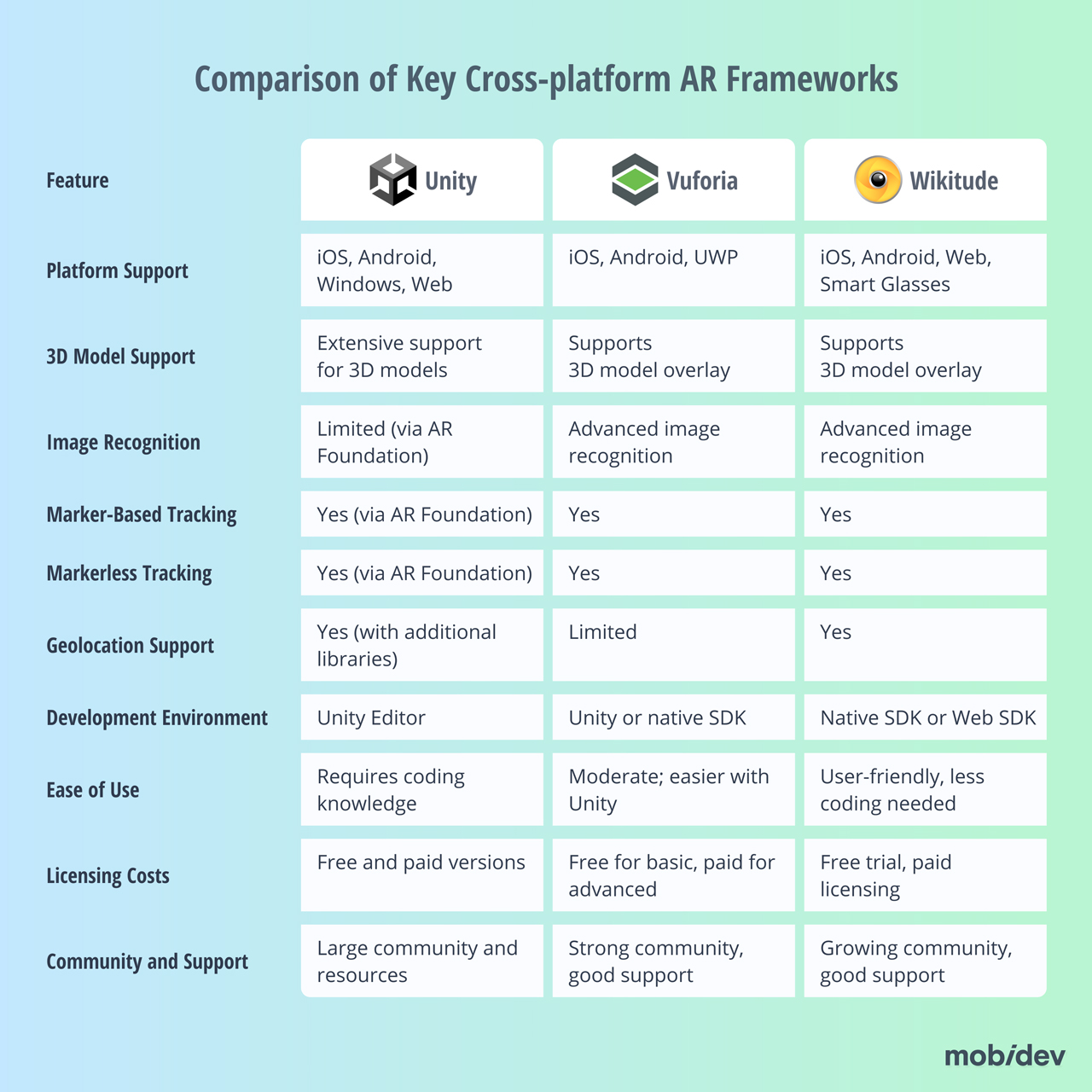
There are a few cross-platform frameworks available to choose from when developing applications for Android, iOS, and the web. Some options include Unity AR Foundation, Vuforia, and Wikitude. This table highlights compares their respective features and capabilities:
Think carefully about the features that your AR application needs to succeed. You should also consider how much your AR application may change over time. Is the framework you want to choose going to continue being updated over time with the features you need, or will it stay stagnant?
WebAR for AR App Development
The most flexible and widely compatible AR solution is WebAR. It has the advantage of running on almost any device without installing additional software. However, this means its capabilities are limited to basic applications. Many businesses utilize this for simple tasks like virtual fitting room features. Brands like Maybelline, L’Oréal, Target, and more have used WebAR to demonstrate products using a front-facing camera viewfinder.
WebAR can accomplish tasks like facial recognition filters, changing the colors of surfaces and objects, as well as replacing and blurring backgrounds when videoconferencing. However, it cannot provide the same level of quality, fidelity, and performance as native mobile AR applications.
Starting your project with AR consulting can help you make more informed decisions about technologies and platforms that will help you achieve your business goals.
Interested in AR consulting?
Learn moreHead-Mounted Displays (HMDs)
Wearable augmented reality is growing thanks to advancing hardware capabilities from major brands like Meta and Apple. Although traditional development efforts like Microsoft HoloLens have declined, new consumer-oriented devices have taken their place, such as the Meta Quest 3 and Pro lineup. Apple has also entered the ring with its Vision Pro headset. All three of these headsets demonstrate that head-mounted displays (HMDs) are a viable product category that consumers are willing to use.
The Meta Quest device lineup utilizes a modified version of Android. Developing for Quest devices can be done using Unity AR Foundation and Meta OpenXR package. Meanwhile, Apple Vision Pro utilizes similar technologies to mobile iOS AR development, such as ARKit, RealityKit, and SwiftUI.
Regardless of what platform you decide to develop on, it’s important to consider the user experience. Wearable AR experiences are unique because the interface is not as familiar as a mouse and keyboard or a touchscreen. Instead, users might interact using hand tracking, eye tracking, or hand-held controllers. Another point of concern is energy consumption. Immersive HMD experiences are battery hungry. The more advanced your application, the more impact it will have on the user’s battery life.
Artificial Intelligence
One of the most critical supplementary technologies in augmented reality applications is artificial intelligence. AI algorithms can improve AR scene understanding, such as in ARKit’s RoomPlan features. By utilizing machine learning, object detection and scene geometry improves and can be accomplished more quickly than other methods.
AI can also help improve gaps left by ready-made AR libraries. For example, if an AR library lacks solutions for an application like a virtual fitting room, necessary and complicated features like human pose estimation can be enhanced with AI.
Check out our Wi-Fi router diagnostics demo as an example of using a combination of AI and AR technologies.
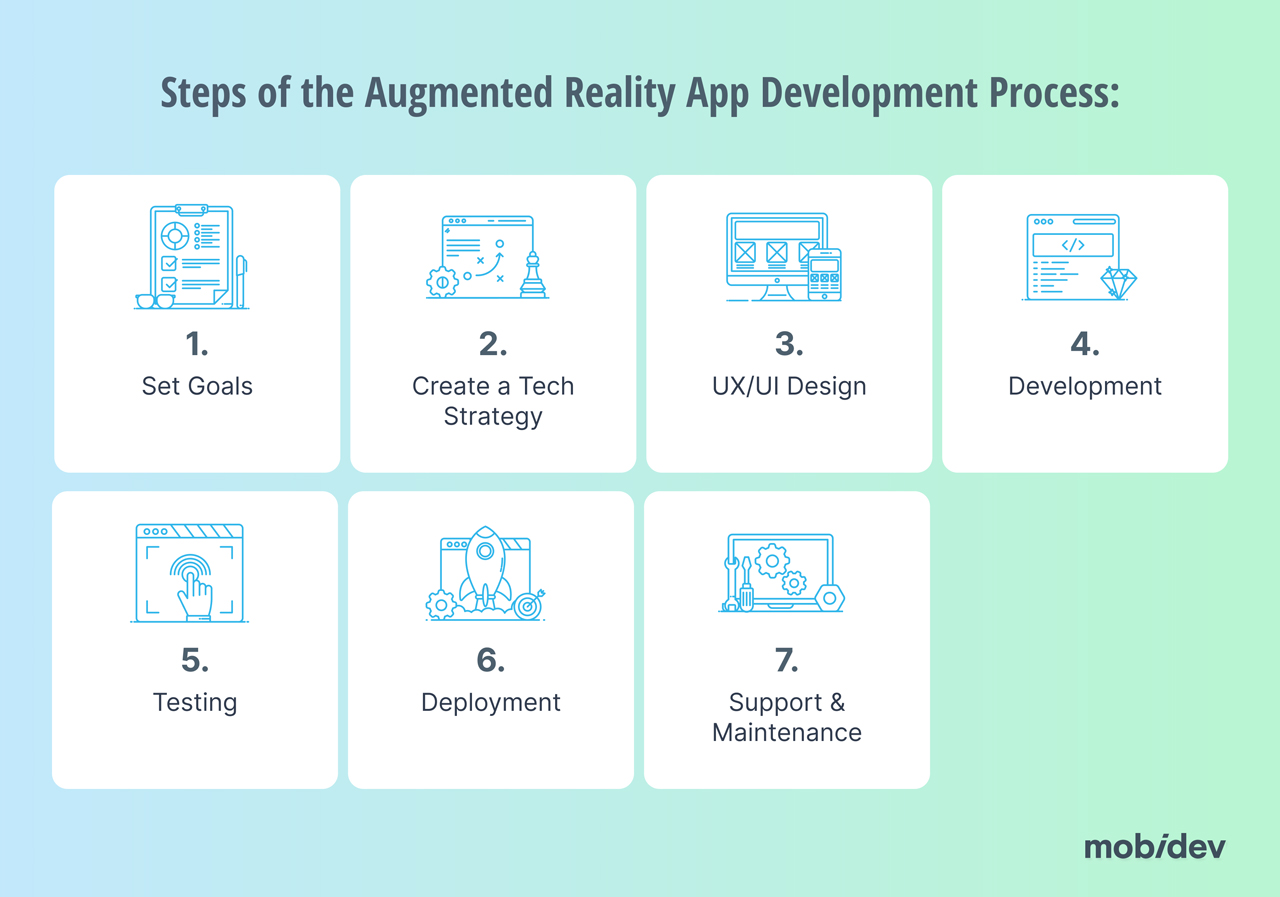
The 7 Steps of Augmented Reality App Development
Now that you’ve gotten a taste for the different technologies and frameworks of augmented reality development, let’s look at what the process of making an application looks like.
Step 1: Set Goals and Requirements
Before you can start anything, you need to have a firm grasp on exactly what it is you want to achieve with an AR application. There are a myriad of questions that need to be answered at this stage, such as:
- Who makes up your target audience?
- What devices do your target audience use?
- What features will your AR application need to utilize?
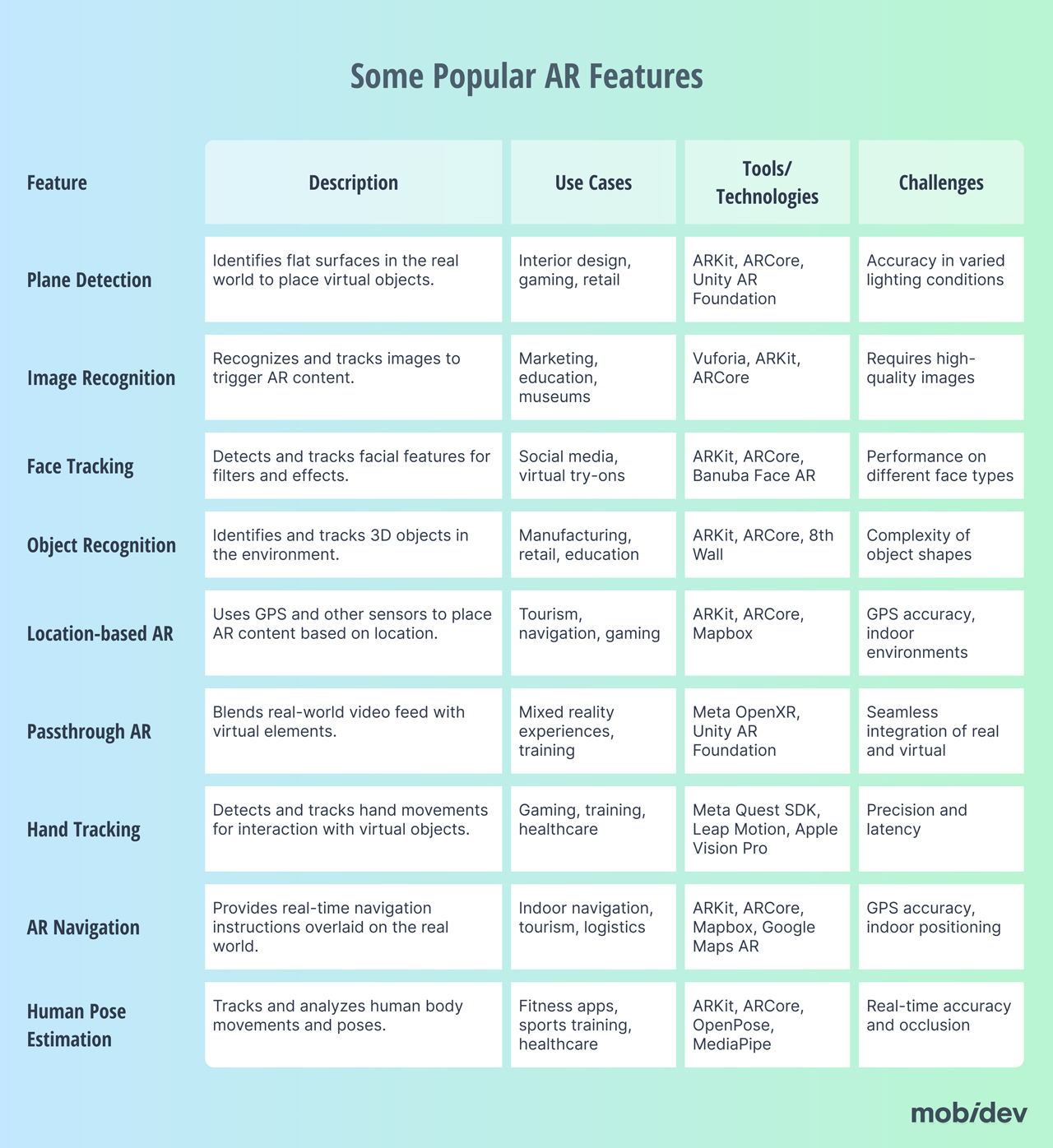
You’ll need to have a vision of not just what the AR application will do, but what it looks like, how it behaves, and how the user will interact with the experience. Here’s a table with some popular AR features that you might consider utilizing in your application:
Step 2: Create Your Tech Strategy
Now that you know what you want to accomplish, you need to figure out how you’re going to make it happen. You’re going to need to account for several key components:
- Choosing development platforms and a relevant tech stack
- Architecture planning
- Decide on whether to use markerless or marker-based AR
You’ll need to decide if your application will need to use markers for its AR experiences. Marker-based AR utilizes landmarks called markers which may be arbitrarily designed 2D shapes, like QR codes. Marker-based AR is cost-effective and provides greater experience stability. However, it’s dependent on whether the markers are visible or not, as well as environmental conditions.
As an example, our team created a marker-based AR indoor navigation application demo that you can check out below.
Markerless AR has much greater flexibility since AR experiences can be generated anywhere, but they can have greater inconsistency in the quality of the experience.
Step 3: UX/UI Design
In this next step, you’ll need to focus on designing the ways that the user will interact and engage with your application. You’ll need to create wireframes and user flows to outline the user’s journey through the app when developing the user experience (UX). When creating the user interface (UI), you’ll need to design the visual elements, ensuring they are intuitive and engaging.
One of the most important aspects of both UI and UX is accessibility. Are all crucial elements and text easy for the user to read? Have you considered how someone with a disability might interact with the application? Think carefully about these questions during the UI/UX design process.
Step 4: Development
Now it’s time to dive into the heart of your project. The development team will need to install all the necessary software dependencies and SDKs. Aside from programming the application, you’ll also need to pay attention to the content your app will provide. You’ll need to develop or acquire 3D models, animations, and other assets.
From here, work can begin on writing the code that will manage the AR functionalities of the application, implementing the UI/UX work, and data management.
Step 5: Testing
As development continues, you’ll need to make sure that your team is assessing their work to verify that features are working as expected. One of the most convenient parts of AR development is that these features can be easily tested virtually in emulators. However, you’ll want to execute functional testing on real hardware in real-life situations as well. In addition, it’s important that you get usability testing from a sample of real users to get feedback that can help improve the experience.
Pay close attention to performance testing. Assess your application across as many diverse types of devices and conditions as possible to get a feel for inconsistencies.
Step 6: Deployment
It’s time to prepare for launch! Ensure that all your application details are finalized and keep your marketing team informed. Where and how you launch your application will depend on where you’re distributing it.
Step 7: Support & Maintenance
After deployment, pay close attention to user feedback. Provide updates and support to the app to correct any issues that arise. You’ll also want to continue performing device testing as new devices enter the market that might be able to run your application. Push out updates to ensure compatibility with your target audience’s devices while maintaining backwards compatibility. You also may want to consider developing new features as technology progresses to enrich the app with new experiences.
What You Need to Know Before Starting an AR Project: Challenges & Best Practices
We’ve covered technologies involved in creating AR applications as well as the development process. However, there are some well-known augmented reality development challenges your team should be familiar with. Let’s talk about how to overcome them and realize your vision for your AR application.
Hardware Limitations
The software is not the only component of the process. The hardware can be just as important to consider. If the hardware of a device isn’t powerful enough, it can adversely affect the performance of your application. Some of these limits include processing power, memory, camera quality, battery life, and other factors.
Device-based optimizations might be required to ensure the best experience. These optimizations might include reducing the quality of 3D models, unloading objects out of view, and other techniques that will depend on your situation.
Tracking Accuracy
Aside from hardware limitations, tracking accuracy can be affected by environmental conditions. Dynamic environments, objects of varied sizes, shapes, and textures, and visibility can all affect tracking. The decision of whether to use visual markers can affect the quality of your tracking accuracy but can adversely affect your application’s flexibility. It’s important to account for what the application should do in less-than-ideal conditions. One option is to detect these conditions and display a warning to the user to inform them of potential errors.
Testing AR Applications
Although emulators are handy for testing AR applications, you need to make sure you test on real hardware too across different environmental conditions. Not only that, but you need to make sure you’re testing on different faces, objects, and anything else that might affect your application. You’ll need special testing strategies to ensure the highest level of quality for your product.
AR Development Benefits Across Industries
Let’s look at some real benefits that businesses can reap from AR applications across multiple industries.
Construction & Renovation
Augmented reality can benefit construction businesses in several ways. For example, AR can help with visualizing a project for clients and investors before work begins. This can help speed up decision-making processes. Companies can also use AR to reduce errors by overlaying BIM models on real-world construction sites. This can help teams identify problems before a project is too far along in development. AR can also help with training simulations to help workers practice necessary tasks and minimize errors.
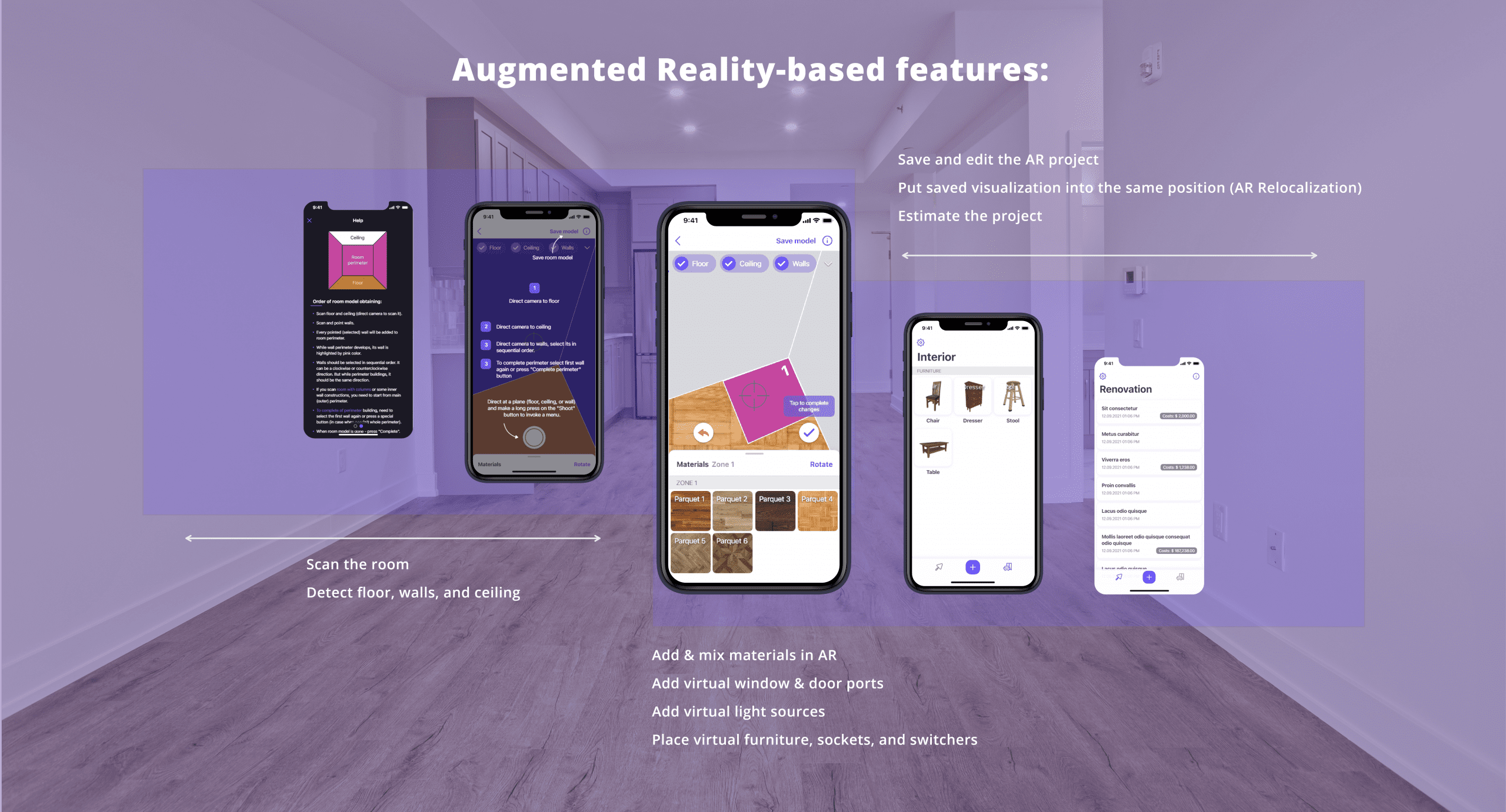
At MobiDev, we developed a Home Scanning iOS app for our client, N2:20. Using ARKit and other technologies, the app helps users visualize room refurbishments and get instant estimates. The app allows users to apply different materials and objects in augmented reality, providing a seamless way to measure and design home improvement projects without physical visits.
Healthcare
Augmented reality in healthcare can help students and surgeons prepare for procedures with AR simulations. AR can also help improve patient care by helping doctors visualize medical treatments and conditions for patients. With appropriate HMD equipment, surgeons can see overlaid, live information about patient vitals while keeping their hands free during a procedure. AR microscopes can also be used to assist with disease detection.
At MobiDev, we’ve been exploring the possibilities of augmented reality for healthcare, which led to the demo of the Augmented Reality Manual for Home Blood Tests.
Retail
“Try before you buy” experiences are extremely popular in the retail industry, and augmented reality provides the convenience of that strategy from a shopper’s smartphone. AR can also provide more engaging shopping experiences, such as in the Ikea app. Ikea’s customers can scan their room and place new furniture and change the colors of surfaces. AR also serves as a creative medium for marketing and engagement, making shopping experiences more memorable and entertaining.
Travel
Augmented reality significantly enhances the travel sector by providing immersive experiences such as virtual tours and real-time navigation, making travel more engaging and informative. It also offers cost efficiency by reducing the need for physical resources through virtual guides and training tools.
Here at MobiDev, we created an AR application for a multinational corporation in the travel industry. The app is designed to engage travelers and increase retention by allowing users to get information on places of interest by pointing their camera, integrating AR with animations, and ticket booking functionality.
Education
Augmented reality (AR) significantly enhances education by providing an immersive experience where students can interact with 3D objects, leading to a deeper understanding of subjects compared to traditional 2D images. It leverages high-resolution learning materials to boost visual learning, helping students absorb information more effectively. Additionally, innovative AR tools capture students’ attention and improve engagement, resulting in increased productivity and performance. AR also offers a risk-free environment for practical training, which is particularly crucial for fields such as medicine and aviation.
How to Build an Augmented Reality App with MobiDev
Finding a team that can execute your vision for an AR application may be one of the most critical steps toward achieving your product goals. Whether you’re updating an existing application or creating a whole new one, MobiDev’s experience is what you need to succeed. With the help of our Augmented Reality consulting services you can navigate uncertainties in the development process and improving your decision-making.
If you already know what you want and are ready to start development, let’s do it! Our AR app development services are here to help. MobiDev augmented reality developers are experienced in combining AR with AI algorithms to achieve more accurate and realistic AR experiences, improve performance, and increase customer satisfaction. All you have to do to take that first step toward success is to reach out to chat.