Contents:
Retail is one of the most competitive industries, which is no secret. Technology here is essential for improving operations and customer engagement.
Geofencing and geotargeting have become quite popular go-to solutions among retailers. They help deliver personalized promotions, enhance in-store experiences, and capture real-time consumer insights.
Since 2009, we at MobiDev have been at the forefront of software consulting & engineering, crafting innovative retail solutions that, among other things, incorporate geolocation technologies.
In this article, I will guide you as a decision-maker through the benefits, implementation strategies, and hidden potential of geofencing for SaaS retail platforms. Leveraging my 12+ years of experience in mobile development, I will provide field insights to help you harness this technology effectively.
Let’s explore why geofencing matters in retail and how it drives measurable results.
Why Geofencing Matters for Retail Businesses
Geofencing is a location-based technology that uses virtual boundaries to trigger real-time actions (notifications, data tracking, or automation) when a device enters or exits a defined area. The geofencing technology helps businesses address the rise in consumer demand for personalized experiences in offline shopping.
A recent study indicates that over half of customers want smarter shopping practices. There is a clear preference for customized and AI-driven personalization that offers the highest convenience, and is, in general, more efficient.
The demand for personalized, real-time experiences is especially high among higher-income shoppers. The study indicates that 59% of consumers earning over $100K seek highly personalized retail experiences. This shift underscores the value of geofencing as a powerful tool for delivering location-based engagement.
That’s why integrating geofencing into SaaS products can significantly strengthen your differentiation in the market. Leveraging geofencing, retailers can achieve key competitive benefits, including:
- Creating hyper-local marketing campaigns
- Delivering personalized offers that are based on real-time location data
- Enhancing customer engagement through relevant interactions.
These improve customer satisfaction, drive sales, and add to brand loyalty.
So how does geofencing work in retail?
Use Cases of Geofencing for Retail Businesses
Geofencing actually revolutionizes retail in various ways. Below are our favorite use cases of how it can benefit your business.
1. Personalized Marketing Campaigns
Geofencing allows for sending push notifications or special promotions to customers when they enter specifically designated geographic zones. In theory, this helps in persuading to make a purchase.
For instance, Starbucks uses geofencing to send personalized offers to customers as they come close to a store. These offers invite Starbucks app users to visit the nearest location and get, say, their favorite banana latte, increasing both foot traffic and sales.
There’s an even more creative example – Burger King’s “Whopper Detour” campaign, which boosted their app downloads by 1.5 million. The campaign offered customers a Whopper burger for just one cent if they were within 600 feet of a McDonald’s location and downloaded the Burger King app.
After you placed an order, the app would show you the way to the nearest Burger King. This resulted in their app becoming the most downloaded one in the Apple App Store for several days. And of course, the number of restaurant visitors rose significantly.
2. In-Store Customer Analytics
Geofencing can be used to track when customers enter or leave specific areas within a mall. It helps retailers analyze foot traffic and engagement. However, due to geofencing’s minimum radius of 100 meters, it is not precise enough to track detailed movement patterns inside a store using GPS only.
The effectiveness of geofencing increases when combined with other technologies. Bluetooth beacons, Wi-Fi tracking, and cameras can provide more precise in-store movement data. This allows for detailed analytics.
Retailers like Walmart may leverage geofencing alongside these technologies to optimize store layouts, analyze foot traffic, and deliver personalized promotions at the right time, creating a seamless blend of location-based insights and customer engagement strategies.
3. Operational Efficiency
Geofencing can improve operational efficiency by triggering location-based actions. This may include notifying staff when they enter or leave store zones. For real-time tracking of employees or inventory movement, additional technologies like indoor positioning are required.
Retailers like Home Depot combine geofencing with indoor positioning to optimize staff deployment and stock management in high-demand areas. This way, they ensure efficient store operations and improved customer service.
4. Omnichannel Retail Experiences
For startups and modern retailers, geofencing helps bridge the gap between offline and online shopping. You can create seamless omnichannel experiences by integrating geofencing with mobile apps. Customers can check stock availability, receive personalized recommendations, or even make purchases while browsing offline in-store.
Nike uses geofencing to notify users about product availability and promotions when they enter a store, which allows them to seamlessly switch between online and in-store shopping.
How Does Geofencing Work? A Look Under the Hood
Geofencing operates by creating virtual boundaries around specific locations using GPS, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and RFID (or Radio-frequency identification, which means using small radio frequency identification devices to track and identify objects).
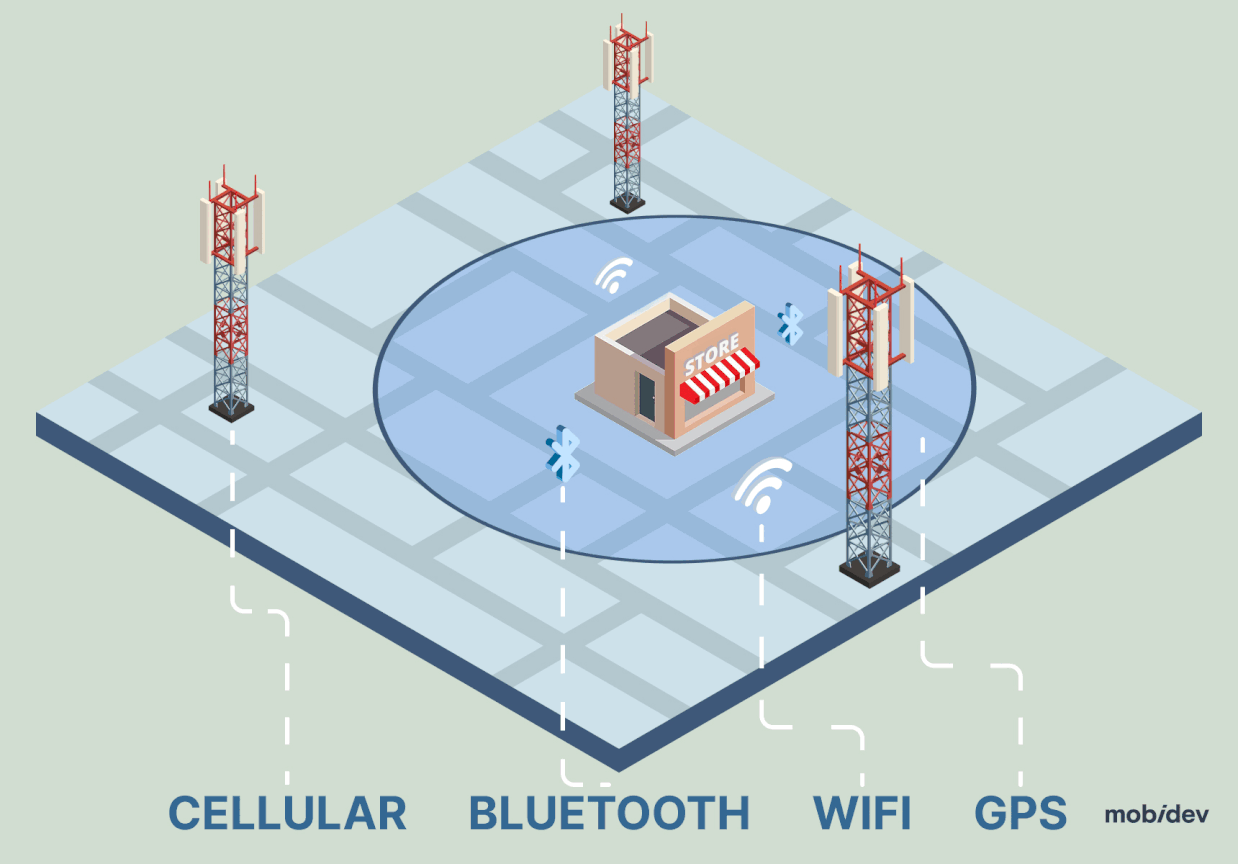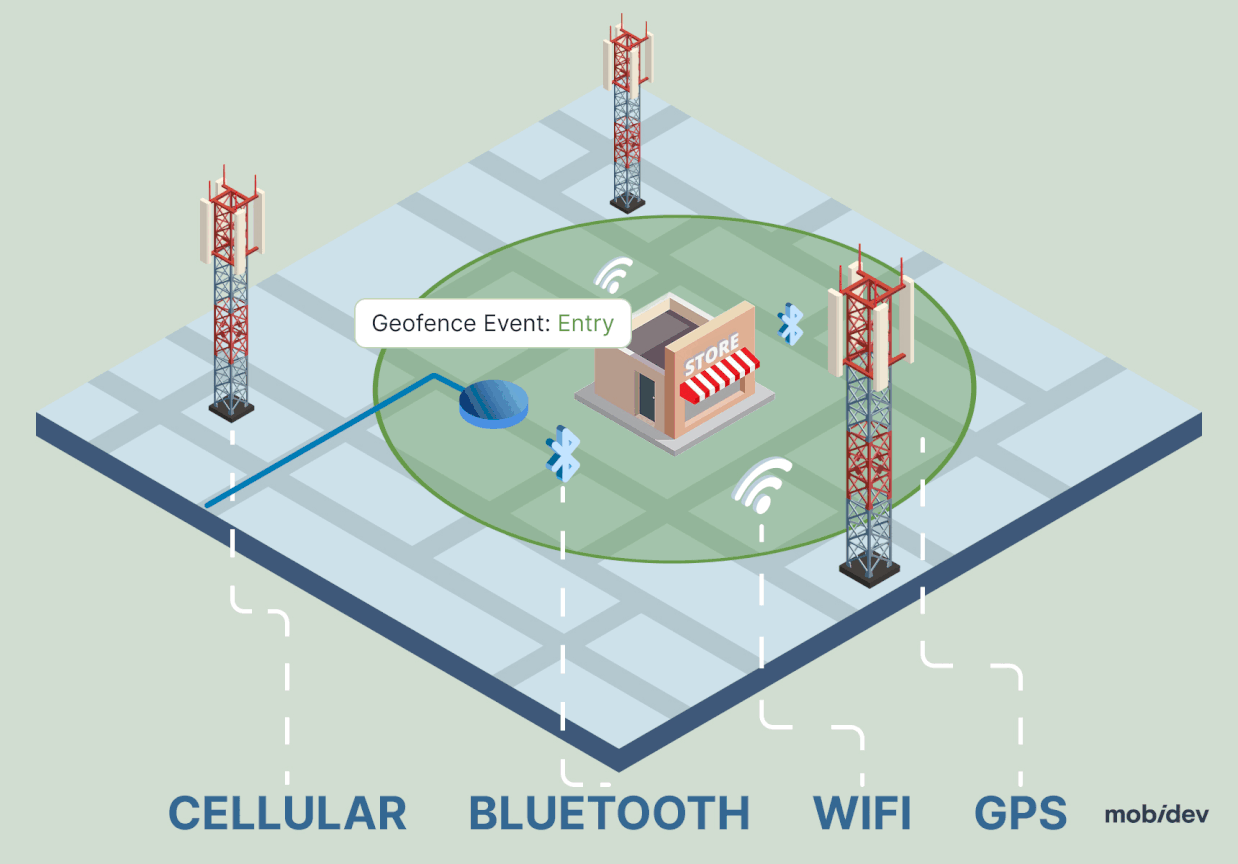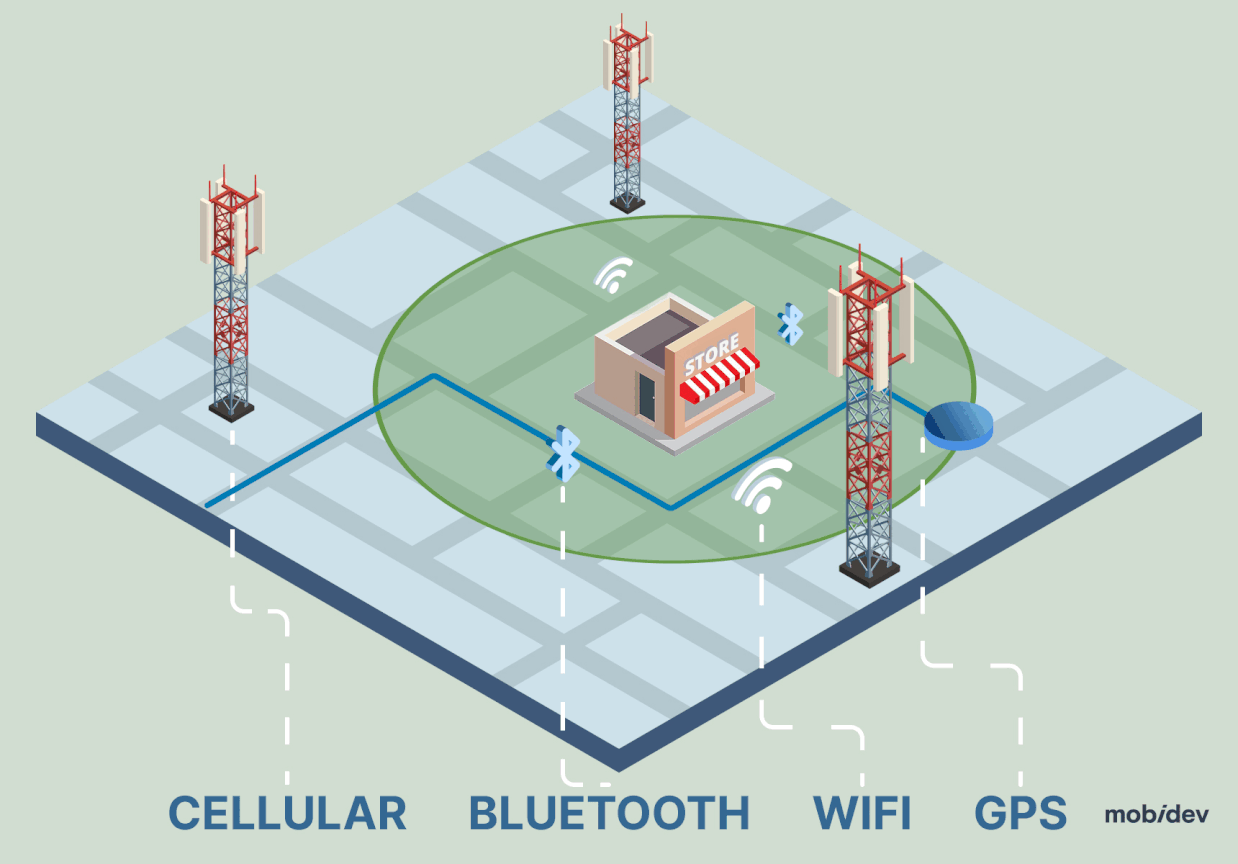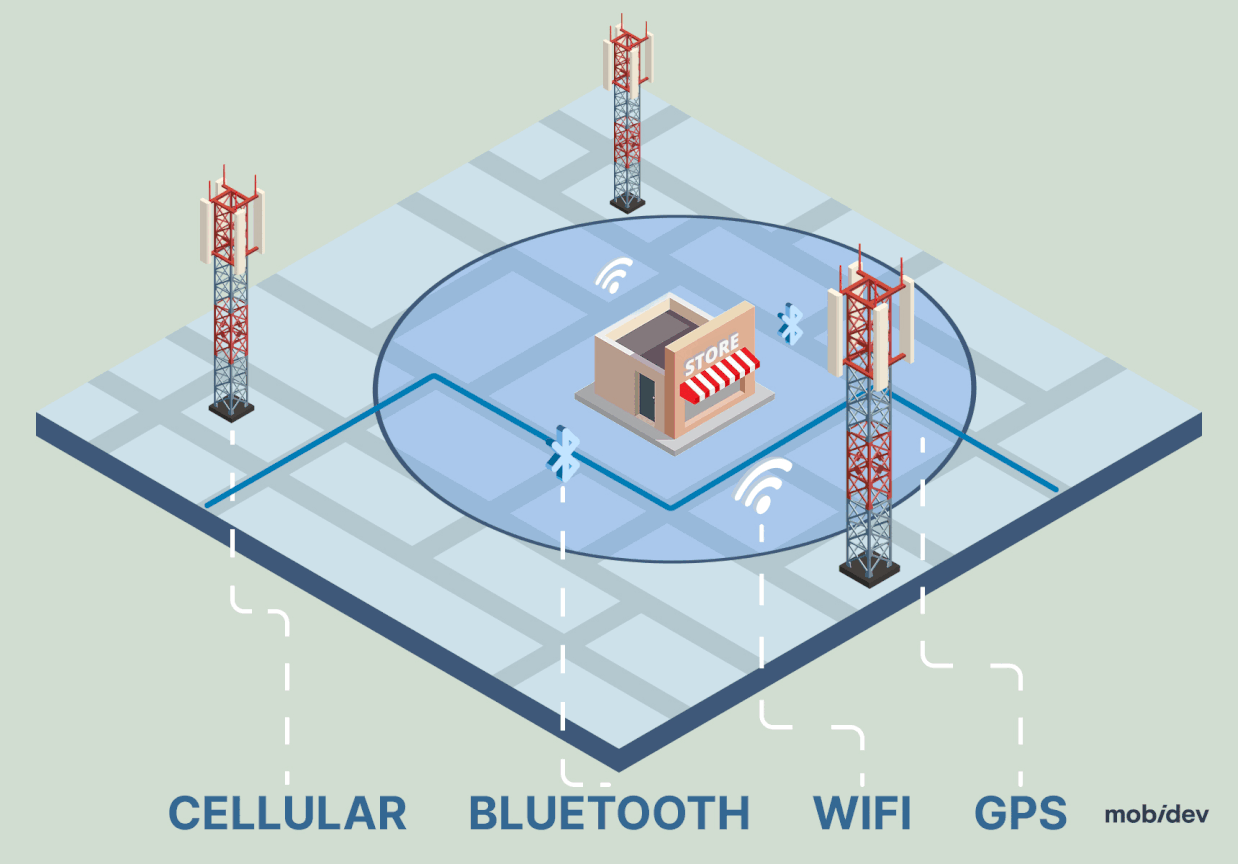
A developer or administrator creates a virtual circle around a location using GPS or Bluetooth software.
More commonly, geofences are created by drawing a circle around a location in tools like Google Maps via APIs. When a device enters or exits this circle, a preconfigured action is triggered, as defined by the admin or developer.
For integration into a retail SaaS product, this involves embedding geofencing functionality into a mobile app.
When the user enters or exits the predefined area, the system triggers notifications or actions in the app. The technology can be easily managed through an online dashboard or API.
Technically, geofencing is most effective in larger outdoor spaces, tracking circle regions with a 100+ meter radius. In addition, as geofencing uses GPS, keep in mind that the signal may be blocked by buildings in downtown areas.
Wi-Fi or cellular data may be needed for further actions after the geofencing trigger is sent. But the technology itself does not rely on those signals, as it works with GPS and/or Bluetooth beacons.
A good example would be Apple’s Find My app, which triggers a notification when a user’s device enters or leaves a specific area. So you know when you may have lost your AirPods. This can work even in flight mode.
Geofencing vs Beacons vs Geotargeting
When looking for a geofencing integration for your app, you’ll likely encounter terms like beacons and geotargeting. These technologies all support location-based interactions but each has some specific features, and therefore, different applications.
The technological differences of all three impact use cases and the complexity of development.
- Geofencing uses so-called virtual boundaries that are defined by developers and are tracked by various signals (like GPS) to trigger actions when a device enters or exits.
- Beacons are devices that use Bluetooth and send signals to nearby smartphones for more precise but short-range interactions.
- Geotargeting focuses on delivering content or ads based on a user’s location, typically using broader data, like an IP address.
While geofencing and geotargeting offer bigger coverage, beacons provide highly accurate proximity-based targeting.
Below is the comprehensive table that indicates the key characteristics of these three technologies.
| 1 | Geofencing | Geotargeting | Beacons | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Technologies used for collecting data | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Cellular, RFID | Obtaining IP-address | Bluetooth |
| 3 | Typical range | Medium: Store, block, district | Big: City, state (using ZIP code) | Small: Specific store departments, metro stations, etc. |
| 4 | Targeting in real-time | + | - | + |
| 5 | Typical platform | Mobile apps | Browsers | Mobile apps |
| 6 | Collecting location data | + | _ | + |
| 7 | Requires hardware | - | - | + |
Taking all these specifications into account, geofencing is a suitable technology for location-based marketing in apps. It allows working with smaller ranges than geotargeting, while not relying on the use of hardware, as beacons do.
Enhancing geofencing with AR and AI
As many mobile devices evolve into wearables and seamless accessories, integrating geofencing and augmented reality is expected to shape the future of actual reality. This fusion will most probably cater to growing customer demands for a more personalized shopping experience with an emphasis on digital.
Geofencing and AR
Geofencing and augmented reality technology (AR) together create interactive, immersive marketing that boosts customer engagement.
As we’ve already discovered, geofencing utilizes virtual boundaries around a specified location to trigger actions when a device enters or exits the area. Combine this feature with AR, and you get to deliver personalized, interactive experiences in real time. This enhances the appeal and effectiveness of branded marketing campaigns.
How so?
AR overlays digital content onto the physical world, creating interactive experiences that easily captivate consumers. In the context of geofencing, AR can provide unique opportunities like virtual try-ons in retail.
The combination of geofencing and AR offers several key benefits.
Benefit 1: Personalized Experiences
With geofencing, marketers can deliver location-based AR content that aligns with a consumer’s real-time context, offering tailored experiences. For example, allowing consumers to virtually try on the clothes that are physically available in the exact store.
Benefit 2: Improved In-Store Navigation
Geofencing combined with AR navigation and Bluetooth beacons enhances in-store wayfinding by integrating precise location tracking with interactive AR elements.
Initially, the smartphone’s position and orientation are established using image tracking of reference markers. Once the position is set, real-time updates of movement are provided through sensor fusion and spatial tracking, displaying the user’s trajectory and guiding them with 2D maps and AR arrows.
Geofencing triggers notifications at points of interest, and users can input destinations to generate routes. To maintain accuracy, periodic corrections are made using reference markers to minimize errors. Note that this use case is only possible with additional technologies like reference markers or Bluetooth beacons because the GPS-based geofencing minimum radius is usually 100 m. So you cannot expect it to work for in-store navigation without additional data tracking.
Benefit 3: Increased Engagement
AR content, when triggered by geofences, encourages deeper interaction, making campaigns more engaging. Augmented reality still feels new for customers, which means creative marketing can prompt people to use the in-app AR right in the store.
Benefit 4: Enhanced Brand Recall
The immersive nature of AR makes the experience more memorable, helping brands stand out. There are not that many AR-powered campaigns yet. Combining a new and creative one with a customer physically present at a store where all the branding is in place promises increased brand trust.
Benefit 5: Actionable Insights
Geofencing provides location data, while AR enables deeper tracking of user interactions, helping marketers optimize campaigns. The data can be reused for remarketing or personalized email campaigns.
For successful implementation, brands should define clear objectives, strategically choose geofencing locations, design engaging AR content, and continually optimize based on performance metrics.
As AR and AI technologies evolve, the potential for geofencing will continue to grow, offering exciting opportunities to engage customers at specific locations and drive meaningful interactions.
Geofencing and AI: How Machine Learning Makes Geofences Smarter
Combining geofencing with AI unlocks marketing possibilities that once seemed impossible. Retail businesses can now deliver hyper-personalized marketing campaigns to practically all of their customers while spending most of their time and resources only on the implementation.
AI allows geofences to evolve beyond static geo boundaries, enabling dynamic and smarter responses based on real-time data. By analyzing patterns in user behavior, AI-driven geofencing can predict people’s movement, optimize actions in apps, and improve promo accuracy, providing a more seamless and personalized experience for users.
This fusion of geofencing and ML opens new possibilities for businesses, enhancing engagement, marketing efforts, and operational efficiency.
A particular example would be how geofencing technology, when combined with AI, is revolutionizing last-mile delivery. Traditional geofencing had limitations, particularly in expansive areas, leading to inaccuracies in dwell time tracking, accessorial fees, and inefficient routing.
However, AI enhances this by using machine learning, such as DBSCAN clustering, to generate precise geofences based on historical delivery data. This results in optimized delivery zones, accurate tracking, and improved routing efficiency.
Industries such as e-commerce, freight, food delivery, and courier services are seeing real benefits – lower costs, better service, and happier customers. AI-driven geofencing is reshaping global logistics, making it more efficient and affordable.
This enhances app relevance and user engagement, although constant location tracking may impact battery life. The app ensures high accuracy in location detection and boundaries, while also prioritizing user privacy and data protection.
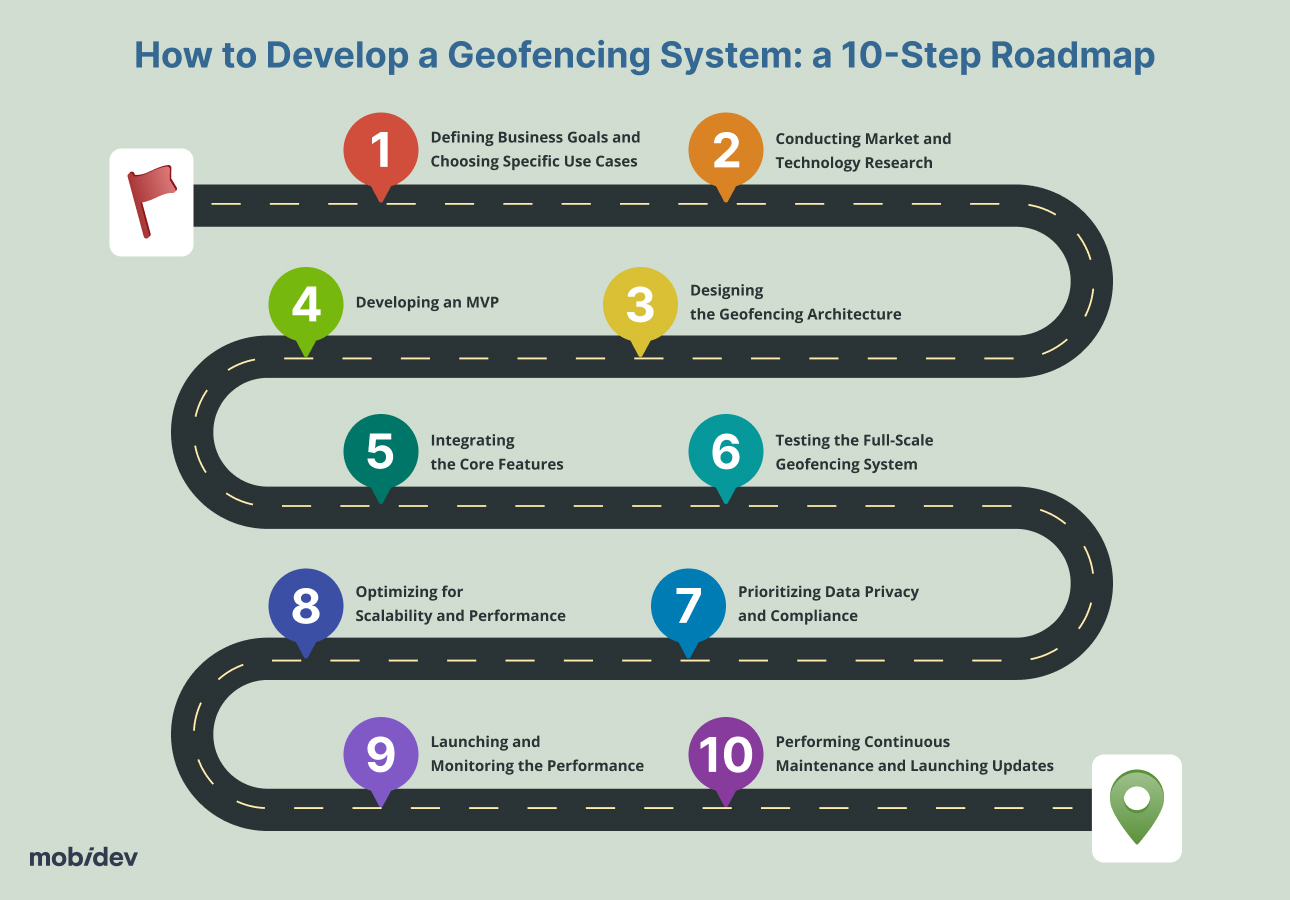
How to Develop a Geofencing System: a 10-Step Roadmap
As you may have guessed from what I’ve shared so far in this article, implementing geofencing can be quite a complex process. However, it’s easier to understand and work with when described in a clear roadmap.
Here’s what a geofencing roadmap should look like.
Step 1. Defining Business Goals and Choosing Specific Use Cases
- Get a clear understanding of what business problems you need to solve with geofencing. These may include, for example, improving customer engagement, implementing in-store analytics, or increasing operational efficiency.
- Determine the use cases that will help solve these problems. For instance, proximity marketing, real-time notifications, or location-based analytics.
Step 2. Conducting Market and Technology Research
- Analyze how your competitors use geofencing (if at all) and find out the differentiation opportunities you can work on.
- Identify how your target audience perceives location-based data usage and privacy.
- Evaluate how compatible your current systems and infrastructure are with geofencing and develop a clear understanding of technical feasibility.
Step 3. Designing the Geofencing Architecture
- Choose the geofencing technology that will best fit your needs (GPS-based or Bluetooth beacon-based).
- Plan on integrating geofencing with your backend systems and understand data processing and analytics practices.
- Choose the cloud services (e.g., AWS Location Service or Google Maps Platform) that would be most scalable to handle location data.
Step 4. Developing an MVP
- Build a minimal viable product (MVP) for testing the core geofencing functionalities and how they work in your systems.
- Roll out specific features like zone setup, event triggers, push notifications, and basic analytics.
- Gather feedback from internal stakeholders or select clients. Identify possible issues and bottlenecks.
Step 5. Integrating the Core Features
- Geofence Setup: Enable clients to create and manage geofence zones within the SaaS platform.
- Real-Time Notifications: Configure event triggers to send push notifications or alerts when users enter or exit geofenced areas.
- Analytics Dashboard: Develop tools for reporting that will analyze geofencing-related data, such as offline customer behavior and campaign performance.
- API Integration: Ensure seamless connectivity with third-party systems (e.g., CRMs, marketing tools, or payment systems).
Step 6. Testing the Full-Scale Geofencing System
- Functional Testing: Ensure geofences activate properly and notifications are triggered accurately.
- Performance Testing: Check that the system can handle high volumes of location data and users at once.
- Compatibility Testing: Test on different platforms and devices to ensure the best customer experience.
Step 7. Prioritizing Data Privacy and Compliance
- Secure and encrypt the users’ private location data.
- Ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR, CCPA, or local privacy laws.
- Create transparent user opt-in and opt-out options specifically for location tracking.
Step 8. Optimizing for Scalability and Performance
- Implement cloud-based services to handle increasing data loads as your user base grows.
- Optimize energy consumption to minimize battery drain on end-user devices.
- Enable dynamic geofencing to manage real-time updates and high-frequency location tracking.
Step 9. Launching and Monitoring the Performance
- Release the geofencing feature to the selected clients or markets.
- Monitor key performance metrics. For example, geofence accuracy, response time, and user engagement rate.
- Make sure to let users leave their feedback and collect it properly to address possible pain points.
Step 10. Performing Continuous Maintenance and Launching Updates
- Make sure to identify and fix bugs or performance issues in a timely manner.
- Consider adding more features, such as AI-based analytics, predictive geofencing, or support of multiple geo-locations. Try to get omnichannel use of geofencing.
- Keep up with recent technology trends and privacy regulations to keep a competitive edge.
This roadmap is a high-level description of what a geofencing implementation strategy should look like. You may, however, face some challenges on each step. So what are the most common difficulties associated with geofencing?
5 Main Challenges When Implementing Geofencing in Retail Products
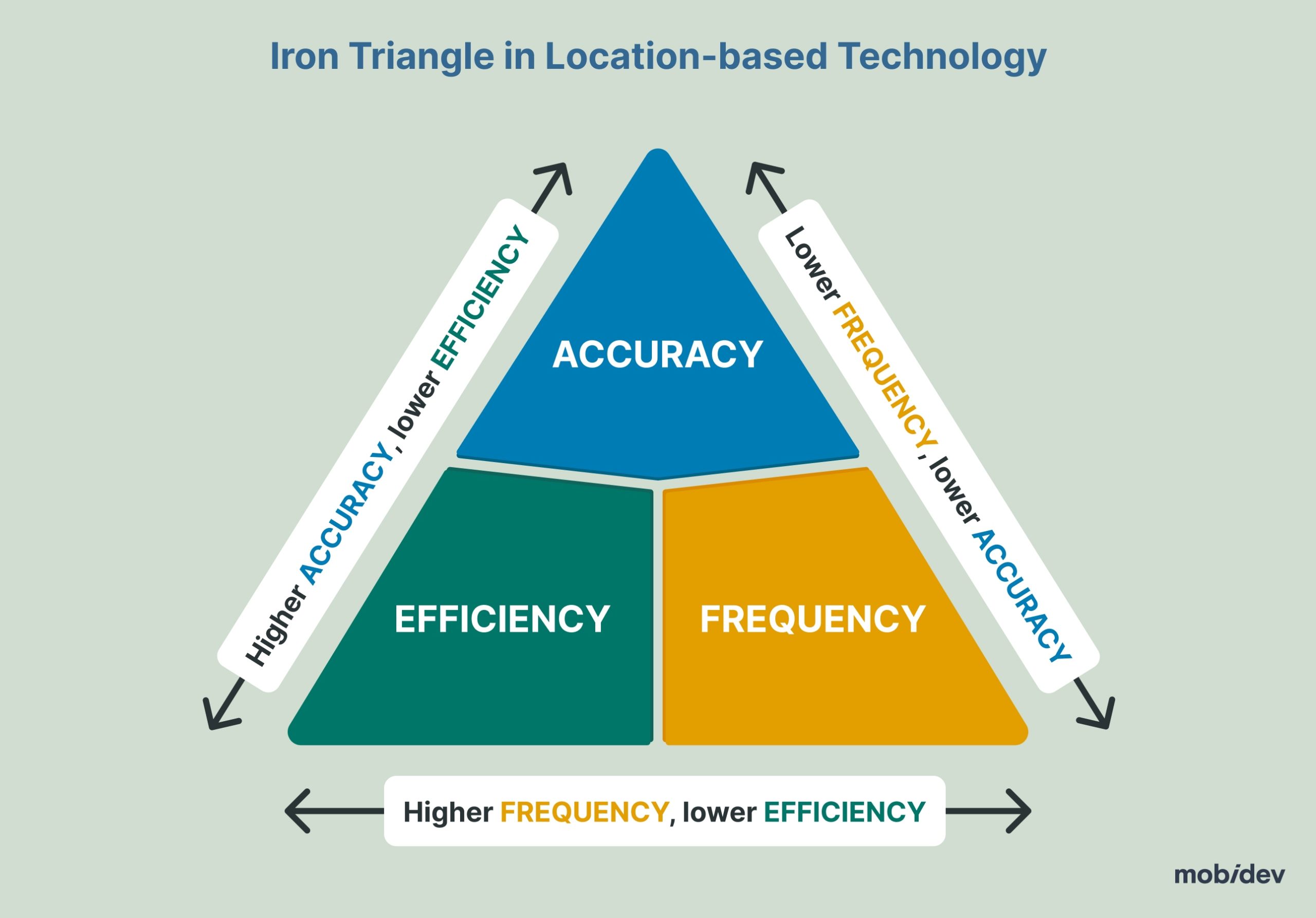
Building location-based experiences requires balancing multiple aspects such as privacy, accuracy, battery efficiency, and user education.
There’s a concept of the Iron Triangle in location-based technology where accuracy, efficiency, and frequency affect each other. Increase the accuracy and users’ batteries will discharge faster. Optimize for longer use, and you lose accuracy, and so on.
Luckily, it’s possible to identify the biggest issues a retail business may face when using geofencing in their product.
1. Choosing the correct geofencing communication protocol
Selecting the right communication protocol for geofencing is crucial to ensure seamless connectivity, accuracy, and efficiency. Different protocols offer varying advantages based on range, power consumption, and real-time responsiveness. Businesses should consider their specific use cases. Whether it is outdoor tracking or indoor asset management that they need the most. Depending on the use case, there are specific protocols:
- GPS Tracking. Ideal for outdoor geofencing with high accuracy
- Bluetooth Beacons. Enable proximity-based geofencing indoors using beacon signal strength
- RFID Systems. Effective for short-range location tracking in controlled environments
2. Keeping location data safe
Protecting user location data is key for trust and legal compliance. Strong encryption ensures sensitive data stays secure, whether in transit or storage. Whenever possible, businesses should anonymize location data to reduce legal risks. Compliance with privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA is crucial, requiring clear policies on data collection, storage, and sharing in geofencing.
Users must also have control over their location data, with straightforward opt-in and opt-out options, as well as easy access to privacy settings. Though it’s not always easy, by prioritizing security and user consent, companies can build trust and maximize the benefits of geofencing.
3. Competitive geofences in urban areas
In dense urban environments, overlapping geofences from multiple businesses can create competition for user attention. Precision in defining geofence boundaries is essential to avoid unintended triggers and interference from competitors’ geofences.
Utilizing AI-driven geofencing can help refine targeting by analyzing user behavior and optimizing trigger conditions. Additionally, geofences should be strategically placed to provide real value rather than simply flooding users with notifications.
Retailers can enhance engagement by leveraging contextual data, such as peak traffic times and user preferences, to deliver timely and relevant geofencing interactions.
4. GPS battery draining
Continuous GPS tracking can quickly drain a device’s battery. However, a key advantage of geofencing is that it doesn’t require constant location monitoring. Instead, it triggers actions when a user enters or exits a predefined area, using a combination of GPS, Wi-Fi, and cellular signals. This makes it more battery-efficient than continuous GPS tracking.
When you do use live location tracking in addition to geofencing, adjusting location update frequency based on user activity can help. For instance, high-frequency tracking should be reserved for when a user is inside a geofenced location and is interacting with the app, while lower-frequency updates can be used when they are stationary or far from a relevant area.
Balancing accuracy and efficiency ensures a seamless user experience without excessive battery drain.
5. Comparing geofencing limitations in iOS and Android
Geofencing capabilities vary between iOS and Android.
- iOS restricts apps to monitoring only 20 geofences at a time, while Android allows up to 100.
- Both platforms have a minimum radius of 100 meters.
- Background geofencing on iOS is usually less reliable than on Android, as the latter has fewer delays and better accuracy.
For polygon tracking, developers can either take a bigger circle zone that covers the target area and some additional area around it or add multiple circle zones to fit inside a polygon. It is also important to point out that cross-platform solutions like Flutter rely on native plugins, which have the same platform-specific constraints.
Despite these challenges, geofencing is still a valuable tool for retail businesses. Choose the right protocols, ensure data security, optimize battery use, and manage platform limitations to create seamless and engaging location-based experiences.
Just like we did with one of our clients.
Success Story: Boosting Fashion Boutique Chain Omnichannel Sales Using Geofencing
Business Goal
Our client, a fashion boutique chain, had a mobile app that allowed ordering sunglasses online with a virtual try-on, which is quite a convenient feature. But it’s also great to have a physical store where people can take a closer look at the glasses. Each customer should have a choice – to visit a physical or an online store. However, there has always been a gap between them, and the client tasked us to bridge that gap.
How we delivered
To achieve this goal, we decided to use geofencing. In its simplest form, it would have been enough to send notifications with special offers when a user was near a physical boutique. For this, iOS app development required using Core Location, and Android app development required the Geofencing API.
However, this still did not fully bridge the gap between the online and offline stores, so we decided to implement a more complex operational logic.
To do this, we needed to collect user behavior analytics within the mobile app and integrate with the inventory management system (IMS) to send relevant notifications.
Thus, we identified three key parameters for user interaction with the app:
- Whether the user has the mobile app installed and has granted notification permissions
- Whether the customer has used the AR virtual try-on feature and for which glasses models
- Whether the user has added any models to their favorites
Additionally, we considered two possible inventory statuses for a specific model in a given store:
- Available in stock
- Out of stock
| 1 | App is installed | AR virtual try-on action | Favorites action | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Available in stock | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| 3 | Out of stock | 1 | 2 | 2 |
According to the table:
- If a user has installed the app but has not actively interacted with it, this is Priority 1. The current stock in the store doesn’t matter because we don’t know the customer’s preferences. In this case, a general notification can be sent.
- If a user has tried on glasses via AR or added a specific model to favorites, but that model is not available in a nearby store, this is Priority 2. Even though the preferred model is unavailable, the customer might be interested in other options.
- If a user has tried on glasses via AR and they are available in a nearby store, this is Priority 3. As there’s a high chance that the user is interested in this model, it’s worth encouraging them to see it in real life.
- If a user has added a specific model to favorites and it is available in a nearby store, this is an ideal match with the highest purchase probability – Priority 4. In this case, a highly targeted notification is sent.
Of course, we also track whether the user has already purchased the glasses online. If they have, there’s no point in promoting the same model in an offline store. Instead, these users receive different messages with special offers for loyal customers.
Business results
The geofencing solution enabled the client to send highly targeted promotional offers, leading to measurable improvements in both sales and customer satisfaction:
1. Boosted sales after virtual try-on online
Integrating the virtual try-on with geofencing helped in increasing in-store purchases by 23% among users who received personalized notifications. The online-to-offline conversion rate also grew by 17%, as customers were more likely to visit the boutique and finish their purchases there.
2. Increased customer satisfaction
Personalized notifications led to 11% fewer app uninstalls and a 12% improvement in customer satisfaction scores. This is likely due to users appreciating receiving relevant offers rather than getting some generic advertisements.
Build Your Own Geofencing System with MobiDev
MobiDev’s team brings our deep expertise in retail software development and complements it with location-based services proficiency. It makes us a trusted company for building geofencing systems created specifically for your needs: all the way from identifying the strategy to implementing every minute detail in it.
Since 2009, we have helped businesses integrate AI, AR, and IoT technologies to create innovative and scalable solutions that achieve positive ROI from the get-go. Whether you need technology consulting or full-cycle development, our team can support you at any stage of your journey.
We prioritize long-term cooperation too, as we believe this ensures sustainable value and continuous improvement. Our experience in the retail industry allows us to develop secure, high-performance solutions that improve customer engagement metrics and add to operational efficiency.
Learn more about our retail software development services or contact us to discuss your needs for geofencing expertise.