Contents:
If there’s one thing I’ve learned from working with ERP systems, it’s that no two businesses have the same needs. Some companies get by with outdated software, even though it holds them back. Others are constantly looking for smarter, AI-powered ERP solutions that can scale with their growth. The real challenge? Finding the right mix of flexibility, performance, and functionality.
I first got into ERP software development while working on ComCash. What started in 2013 as a locally-based POS solution evolved into a modern, industry-recognized cloud solution through our development efforts. Since then, at MobiDev, we’ve helped businesses move away from inefficient legacy systems, integrate AI-driven features, and build custom ERP solutions that actually make a difference in daily operations.
Whether you’re upgrading an old system, creating an ERP from the ground up, or adding new capabilities, this guide will walk you through the process step by step.
What is ERP Software?
The main goal of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is the integration of the various subdivisions of a business within a single application. Unlike having different apps for specific areas of business like finance, HR, sales, and supply chain, an ERP system integrates all of them. This leads to increased productivity and optimization of workflows. It also minimizes duplicate efforts, reduces errors, and offers valuable insights, enabling businesses to mitigate losses more efficiently.
In the absence of ERP, companies have to proficiently deal with separated volumes of data, slow systems, and endless bottlenecks which all make timely decision-making a nightmare.
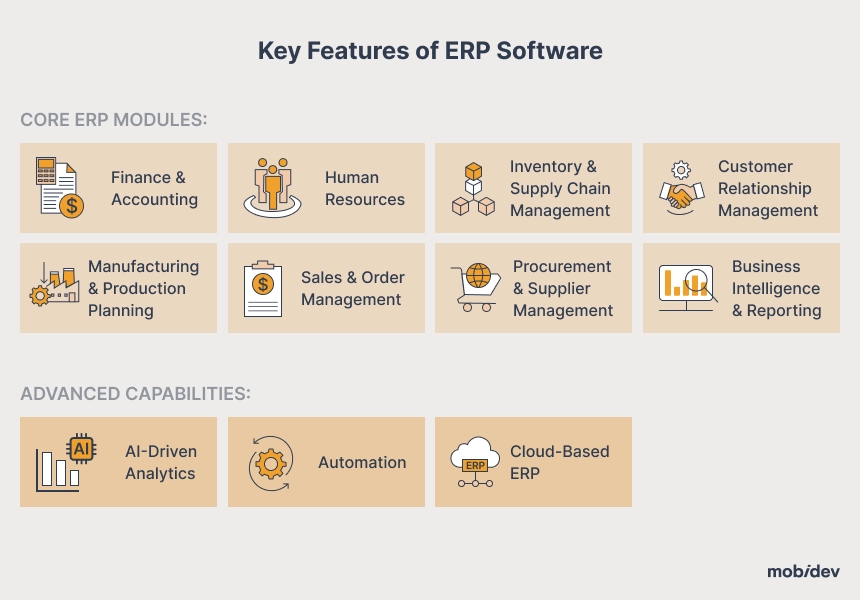
Key Features of ERP Software
Although ERP solutions may vary in scope and depth, every well-crafted solution must contain at least two key elements: high-quality core modules that fully automate operational business processes and advanced capabilities that enhance productivity. Let’s analyze these features in detail.
8 Core ERP Modules
1. Finance & Accounting – This part is considered the most critical module of an organization. Some of the key features of ERPs include automation of bookkeeping, tracking of transactions, managing the cash flow of a business, and taxation compliance. An organization is given the capability to manage its business expenditures accurately, ensure that reliable financial statements are issued, and predict future expenditures, resulting in stability.
2. Human Resources (HRM) – Employing workers and managing them well is equally important for the growth of any business. The HR module covers the entire payroll administration, employee benefits, recruitment, and performance appraisal systems. Through self-service portals, employees can view their pay stubs, submit leave requests, and make personal data updates, reducing the HR workload to a great extent.
3. Inventory & Supply Chain Management (SCM) – SCM is about striking a balance between having adequate stock on hand and avoiding overstocking or stock shortages. The SCM module monitors stock movements in real-time as well as optimizes space within the storehouse. It also links suppliers to the logistics for more effective procurement and delivery services.
4. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) – Determining customer needs is imperative to increasing sales in the company. A CRM module assists users in monitoring customer interactions and lead management. Businesses receive an opportunity to study a customer’s purchase history as well as other preferences more effectively. Why does it matter? The reason is that this information can help them improve strategic marketing and customer satisfaction later on.
5. Manufacturing & Production Planning – This module is particularly important for production-oriented companies. It assists with activity scheduling, materials and equipment management, and efficient resource allocation. Through integration with inventory and procurement systems, manufacturing processes are enabled seamlessly without delays and additional unwanted costs.
6. Sales & Order Management – The entire sales cycle, from order placement to invoicing, can be automated using this particular module. Automation of these functions allows real-time updating of inventory, minimized billing errors, and faster order fulfillment. Customers receive order fulfillment notifications, which improve the overall buying experience.
7. Procurement & Supplier Management – Businesses are reliant on multiple vendors for raw materials and equipment. This module simplifies vendor selection, manages contract expiry dates, and automates purchase orders. In fact, this module can enhance cost-effectiveness beyond measure through performance assessment analyses and improved negotiation terms.
8. Business Intelligence & Reporting – Without a doubt, these days, decision-making requires access to real-time information. The Business Intelligence module compiles data from several departments and creates tailored dashboards and reports for each division. This helps executives keep track of business KPIs, see movements ahead of time, and deal with all sorts of bottlenecks.
3 Advanced Capabilities of ERP
1. AI-Driven Analytics – The integration of AI into ERP systems comes with new functionalities like predictive analytics and trend-based decision-making. Businesses no longer need to rely on personnel to analyze documents. Here, AI software is capable of analyzing countless trends and anomalies and predicting future needs. For example, AI is able to evaluate purchasing behavior and adjust order quantities accordingly to avoid over-ordering or running out of stock. In particular, AI is able to independently examine and streamline repetitive processes, saving time and increasing precision by identifying fraudulent activities and automating risk evaluations.
2. Automation – Automation is one of the major advantages of modern ERP systems. Operations can come to a standstill because of manual data entry or routine tasks. Automated workflows refine these processes by decreasing the need for human intervention. For example, automation can be used in invoice processing. After the placement of an order, an invoice is automatically generated by the system which updates the financial documentation, while notifying relevant teams.
3. Cloud-Based ERP – Unlike on-premise ERP solutions, having a cloud-based ERP increases the flexibility of the business, allowing it to save on costs. The reason for this is the expensive infrastructure that on-premises require. With cloud-based ERP, employees can access information from any location, which supports remote work and global operations. Also, cloud service providers free up in-house IT personnel from tedious tasks like managing system updates, security patches, and maintenance. Furthermore, cloud ERP solutions provide real-time data synchronization across locations so that all departments are working with the most current information.
How Does ERP Work? 5 Operational Layers
As you already understand, an ERP system serves as the nerve center of a business. It allows for seamless communication between departments, keeps the latest information, and ensures smooth operations. Let’s analyze how ERP functions.
1. Data Centralization
When various groups of people operate with different software applications or their own individual spreadsheets, it’s no wonder that, at times, data may get fragmented and messy, resulting in inconveniences for all. Yet, ERP comes in handy exactly for such cases, as it can integrate everything into a single system, eliminating chaos.
Example: From the sales team’s perspective, there is no need to make a call to the warehouse to check if something is in stock, because it has already been updated in real-time. Meanwhile, finance can see pending invoices without waiting for emails from accounting.
Why It Matters: Having one source leads to improved communication within teams and decision making gets a whole lot easier.
2. Process Automation
Duties such as payroll, invoice creation, and inventory updates are astonishingly time consuming. ERP technology offers greater optimization of tasks through automating processes so that employees can give attention to more intricate matters that require their skillset.
Example: Once a customer places an order, the system updates stock levels, generates an invoice, and notifies the shipping department. All of this happens automatically.
Why It Matters: Having to do less manual input means decreasing the possibility of errors.
3. Seamless Integration
A business runs best when every team is on the same page. ERP connects different functions, ensuring smooth collaboration across departments.
Example: A new hire joins the company. Instead of HR manually updating payroll and sending emails to IT for system access, the ERP handles everything in one go.
Why It Matters: When processes are integrated, the personnel no longer have to constantly check updates. Instead, they have more time to get more important work done.
4. Real-Time Analytics
Having out-of-date reports can put a business at risk in fast-moving industries. Having ERP eliminates this problem, as business leaders can make decisions based on real-time data rather than information obtained last week.
Example: An e-commerce manager sees that a certain product is selling out quickly. They can reorder in advance instead of waiting for the stock to run out. This way, a business avoids lost sales.
Why It Matters: Opting for real-time analytics allows businesses to adjust strategies on the fly to prevent other costly mistakes.
5. Customization & Scalability
ERP systems are built to adapt, regardless of whether your company is just getting started or expanding internationally.
Example: A small retailer might only need inventory and accounting tools but with the application of certain business tools (CRM, AI-powered analytics etc.), they can enhance their client experience to a great extent.
Why It Matters: ERP effortlessly eliminates expensive system replacements down the line, forcing the company to undergo digital transformation in the long run.
8 Industries That Use ERP
Over the years, ERP systems have become an integral part of any kind of business. They have already proven that they can effectively cut down on redundancies and smooth out coordination, and that’s not the whole list of their advantages. But what does that look like in various industries? Allow me to explain.
1. Retail & E-commerce
In retail and e-commerce, all activities revolve around ERP because it integrates all functions into one system. Each sales channel is linked which increases the level of consumer services provided. Whether a retailer wants to track inventory in different locations or streamline order processing, ERP helps to keep everything in sync. Broadly speaking, ERP helps businesses recognize operational lags during demand, and what’s just as important, increase overall customer satisfaction during shopping.
2. Hospitality
When it comes to the hospitality and catering sectors, the application of ERP systems can ensure better management of daily activities and improve the experience of guests and visitors. In particular, choosing modern ERP systems allows businesses to perform more effective booking management, inventory management, or dozens of other administrative activities. Whether you’re in charge of a hotel, a resort, or a restaurant, ERP can redirect your worries to what truly matters.
3. Healthcare
Each healthcare organization has specific interests and ERP systems aim to meet those interests. Patient data and appointments, as well as almost all other administrative functions, can be managed with ease using ERP systems. With ERP, employees will spend significantly less time on bureaucracy. This is how ERP systems help healthcare professionals focus less on paperwork and more on patient care.
4. Manufacturing
When it comes to the manufacturing segment, ERP, without a doubt, has become truly revolutionary. Providing a solution to indisputably intricate production processes whilst maintaining high-quality standards is quite a feat for firms. ERP captures an entire process, which includes inventory monitoring and production scheduling. This system enables better control of resource allocation and smooths out a variety of other activities.
5. Finance & Banking
Enterprise resource planning systems are useful for the finance and banking sectors because accuracy and efficiency are key factors for success in those industries. Modern regulation compliance, financial transaction processing, and risk assessment are some of the processes that ERP aids with. The entire process of invoicing, financial reporting, and payroll are just some of the multitude of tasks that can become fully automated.
6. Construction & Engineering
Like any other industry, construction and engineering companies need to effectively manage their budgets and resources. The use of ERP automates and simplifies the more difficult aspects of project management like tracking time, material usage, and budgeting. From progress monitoring, cost tracking, contractor management, to any other more complex task, ERP systems greatly enhance efficiency throughout the project cycle.
7. Education
Beyond businesses, educational organizations are able to take advantage of advanced ERP systems. From high schools to universities and even training centers, ERP aids both in administrative and academic tasks. Many of the administrative processes like student admissions, grading, and scheduling can be automated through ERP, improving the educational focus.
8. Automotive
To cap it all off, ERP can be beneficial to users in the automotive industry. Automotive manufacturers rely on ERP software to coordinate their production schedule along with inventory and supply chain management. Dealerships also benefit from ERP solutions by boosting sales, service, and maintenance to ensure that customers have a seamless experience at every touchpoint.
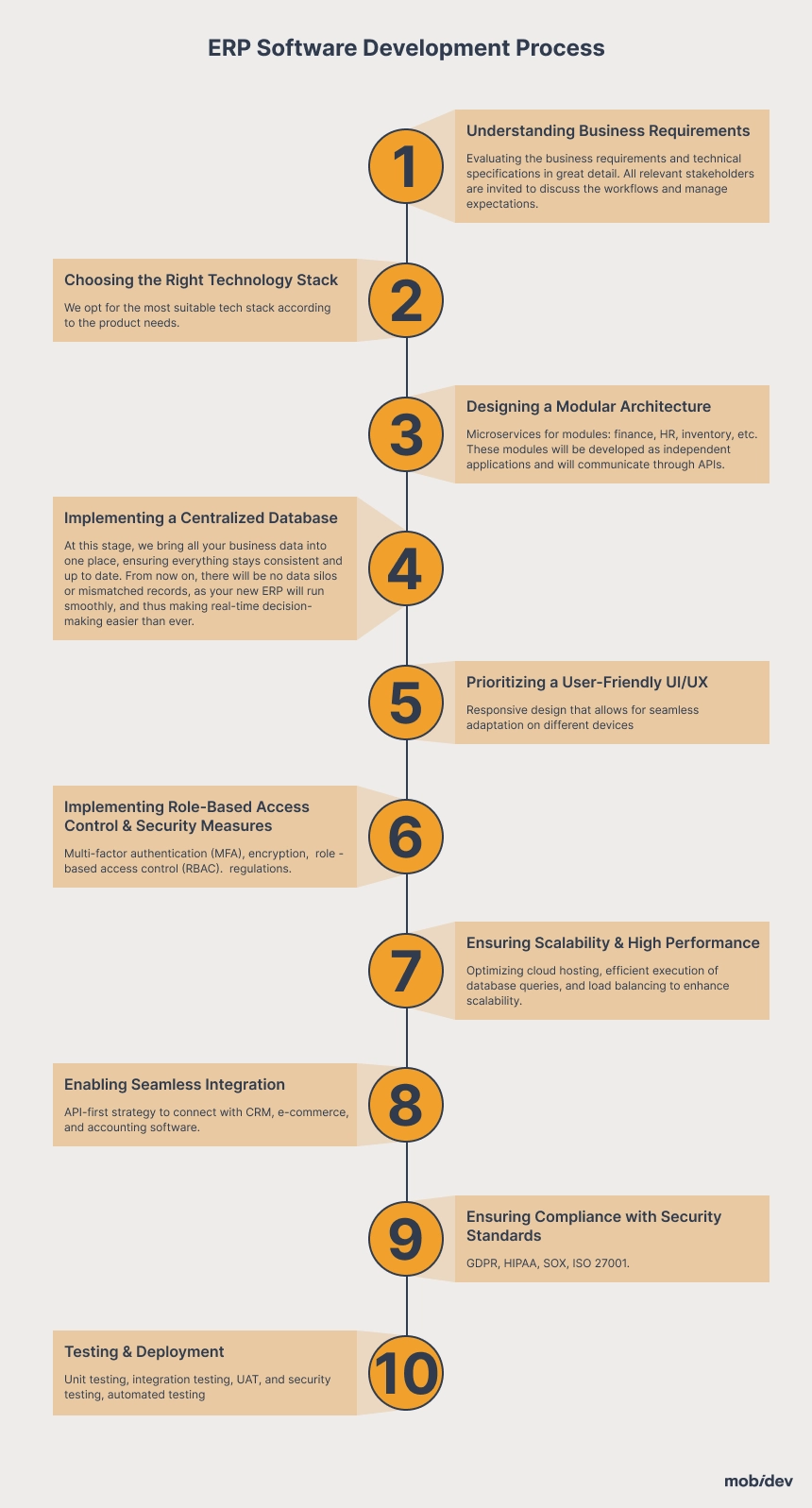
How to Develop ERP Software: 10-Step Roadmap
So how to develop ERP software that stands out? Let me explain the core principles we apply at MobiDev.
Step 1: Understanding Business Requirements
We kick off the development of an ERP system by evaluating the business requirements and technical specifications in great detail. All relevant stakeholders are invited to discuss the workflows and manage expectations. An initial approximation of GDPR and HIPAA compliance is also considered.
Step 2: Choosing the Right Technology Stack
Now, when all requirements are clearly defined, the selection of a technology stack becomes the next step. At MobiDev, we understand that the selected technologies have a solid impact on the system performance and scalability, and that’s why we attempt to opt for the most suitable tech stack according to the product needs.
Step 3: Designing a Modular Architecture
A well-developed, flexible architecture is the central part of every ERP system. In this part, our team implements microservices for modules: finance, HR, inventory, etc. These modules will be developed as independent applications and will communicate through APIs.
Step 4: Implementing a Centralized Database
At this stage, we bring all your business data into one place, ensuring everything stays consistent and up to date. From now on, there will be no data silos or mismatched records, as your new ERP will run smoothly, and thus making real-time decision-making easier than ever.
Step 5: Prioritizing a User-Friendly UI/UX
The design of the ERP system should ensure that end users do not experience difficulties throughout their journey. Our UX/UI specialists ensure that the interfaces are clear and complemented by full functionality. Along with that, user experience is impacted by responsive design that allows for seamless adaptation on different devices.
Step 6: Implementing Role-Based Access Control & Security Measures
To each of our experts, security is always a great concern when it comes to business data management. To protect your information, we apply multi-factor authentication (MFA), encryption, and audit trail monitoring. MobiDev applies controlled system access through role-based access control (RBAC). With this, you will no longer worry about whether your organization meets industry requirements and regulations.
Step 7: Ensuring Scalability & High Performance
Our engineers work on optimizing cloud hosting, efficient execution of database queries, and load balancing to enhance scalability. We also ensure that system performance during peak activity is retained at optimum levels no matter what.
Step 8: Enabling Seamless Integration
It should be possible to integrate other software applications seamlessly into ERP systems. Therefore, we use an API-first strategy to connect with CRM, e-commerce, and accounting software. This way, businesses become more competitive with the use of AI and IoT automation.
Step 9: Ensuring Compliance with Security Standards
I must state once again that it is crucial to focus on regulations from the perspective of legal security and trust. Drawing from our background in the industry, we make sure there is legal compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, and ISO 27001. Furthermore, business-legal risks are minimized by proprietary APIs and encryption technologies.
Step 10: Testing & Deployment
Before launch, we ensure that there is no deviation in stability, security, and performance benchmarks. Our expert QA team performs unit testing, integration testing, UAT, and security testing to ensure everything is in check. Even after the system launch, we provide monitoring and maintenance services to keep the system running properly as your business needs may evolve with time.
With years of experience, MobiDev experts have perfected automated ERP testing to keep our clients’ projects running seamlessly. It helps catch issues early, ensuring cloud ERP systems stay reliable—even with frequent updates. By saving time and reducing errors, automated testing guarantees that everything works as it should.
Key Challenges in ERP Software Development & How to Overcome Them
Developing an ERP system is never a one-size-fits-all process. Below, I’ll explore 3 primary obstacles modern businesses face these days, including their solutions.
1. When Modernizing Legacy ERP Systems
Lacking modernization, an ERP system can lead to increased maintenance expenses or even limited options for integration with other systems. Additionally, replacements can frequently become a problem as they have the potential to disable operational business functions.
The ideal approach to ERP modernization is a strategy based on phased migrations. Instead of cross-cutting everything at once, businesses can slowly adopt modern ERPs by replacing key modules first (like finance, and inventory management) and expanding gradually over time.
Migration to the cloud is another key step. Transitioning from on-premise systems to cloud-based ERPs can enhance security, scalability, and reduce maintenance efforts needed by an IT department.
2. When Building AI-Driven ERP for Scalability
SaaS startups and other technological companies tend to have a harder time finding the right balance between scalability and innovation. ERP systems should address all operational requirements and still provide the business with the ability to shift to new models.
ERP systems offer numerous features such as automated decision making, intelligent process optimization, and predictive analytics. AI has the capability to determine inventory levels that will result in minimal waste by studying sales patterns, predicting changes in demand, and so assisting the business.
In addition, the implementation of AI in ERP requires the integration of all information into a single source from all relevant company departments. Adequate finance, supply chain, and customer interaction data must be collected and structured to provide truly meaningful insights.
3. When Developing Custom ERP Development for Internal Process Automation
Established companies with complex internal processes tend to face issues with off-the-shelf ERPs that at times don’t cater to unique industry-specific needs. Custom ERP development allows companies to build specific solutions but, at the same time, it poses challenges in terms of cost ROI justification.
Focusing on critical features that directly address inefficiencies is essential to obtain a high return on investment. A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) approach helps mitigate risks by launching essential modules first and expanding based on actual business needs.
Concentrating on critical features that fill primary gaps is vital to ensure maximum ROI efficiency. With a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) approach, risk can be reduced by implementing critical business modules first and scaling outwards according to business demands.
Automation is another key factor. Invoice processing, procurement approvals, and compliance tracking are all eligible for manual error reduction.
| # | Challenge | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Modernizing Legacy ERP Systems | Legacy ERPs cause high maintenance costs, limited integration options, and risk of operational disruption during replacement. | Use phased migrations by replacing key modules gradually; migrate to cloud-based ERP to improve security, scalability, and reduce IT maintenance load. |
| 2 | Building AI-Driven ERP for Scalability | SaaS and tech companies struggle to balance innovation and scalability while ensuring ERPs support all operational needs. | Implement AI for automated decision making, predictive analytics, and process optimization; centralize data from finance, supply chain, and customer interactions to enable meaningful insights. |
| 3 | Developing Custom ERP for Internal Process Automation | Off-the-shelf ERPs often fail to support industry-specific workflows, and custom ERP investments require clear ROI justification. | Focus on critical features to maximize ROI; use an MVP approach by launching essential modules first; prioritize automation for tasks like invoice processing, procurement approvals, and compliance tracking. |
Success Story: Transforming Comcash into a Leading Cloud-Based ERP and POS System
Comcash started as a local POS solution in 2013, aiming to evolve into a cloud-based ERP. MobiDev helped build a scalable SaaS platform with advanced retail management features, enabling seamless omnichannel sales. By 2022, Comcash was acquired by POS Nation and now serves over 3,000 locations with integrated hardware solutions. MobiDev continues to enhance its performance and integrations.
The cloud-based system of Comcash manages retail business functions to increase operational efficiency by merging inventory, customer interactions, warehousing, sales, and accounting into a single unit.
The platform spans web, desktop, and mobile applications, covering everything from centralized management and e-commerce to in-store POS, real-time tracking, warehouse and order management, and a customer display system for seamless retail operations.
How We Built and Scaled Comcash
With a dedicated team of six to eight engineers, we took care of the full development cycle—architecture, feature implementation, and ongoing improvements. The first retail deployment happened in mid-2014, marking the beginning of continuous enhancements to the platform.
Retail businesses need their systems to run 24/7 without disruptions. In order to meet this need, we developed a system that enables instant updates, allowing all POS terminals to be updated with the push of a button.
The integration of an internal API and automation tools brought seamless changes. This advancement reduced regression testing for Comcash from one week to two days, facilitating quicker releases, fewer bugs, and greatly improving system robustness.
The evolution of Comcash from a local POS to a comprehensive cloud ERP system evidenced MobiDev’s tremendous effort toward creating scalable, next-generation software. The continuous improvement of in-system architecture, real-time data processing, and seamless hardware integrations allows us to help retailers equip themselves against the competition with tailor-made tools.
This is what former Comcash CEO Richard Stack said about our years of collaboration in developing the product:
[Together with MobiDev], we’re able to work on a 24-hour development cycle, and we release software repeatedly faster than any of our competitors — and there is no overtime. We could never create what we have with MobiDev in my office in California. The tech market is just too competitive these days. If you are interested in developing a world-class product and working with a great group of friendly co-workers every day, I wholeheartedly recommend MobiDev.
Choosing the Right ERP Development Company
Having a well-structured ERP system ensures that business processes are optimized, but you should remember that it’s your selected development team that can make a world of difference. The team you choose should be knowledgeable in both the technological and practical aspects of business.
Our top notch experts work side-by-side with our customers to integrate new AI technologies into their traditional ERP systems and build custom platforms that are tailored to their specific workflows. Our main focus is to enhance business outcomes by offering practical and easily adaptable solutions like cloud migration, process automation, and improved system security.
Learn more about our ERP software development services or reach out to MobiDev today to discuss developing an ERP system focused on achieving measurable results.