Contents:
AI phone ordering is no longer a hype topic—call volumes, labor shortages, and rising guest expectations make it a competitive necessity. If you postpone adoption, tomorrow might simply be too late. The following guide walks you through what an AI phone ordering system can do for your restaurant, hotel, café, or hospitality-tech product—and how you can roll it out successfully.
This guide was created by two MobiDev experts, Iurii Luchaninov, Solution Architect, Oleg Starostin, JS Team Leader.
With over 20 years of experience in software architecture and a deep focus on generative AI, Iurii Luchaninov has designed intelligent systems that merge technical elegance with real-world functionality. Over the past several years, Oleg Starostin has been actively researching and prototyping AI-driven phone-ordering workflows that automate phone-based ordering and reservation flows. This ongoing work reflects their commitment to bringing cutting-edge AI into everyday business processes, giving you a dependable edge in the fast-moving hospitality innovations landscape.
Voice AI Phone Ordering: Quick Overview
Most hospitality businesses still rely on human staff to handle incoming calls. Every manual phone order costs time, introduces errors, and siphons precious attention away from in-venue guests. A voice AI voice ordering assistant changes that dynamic overnight: it greets callers, understands intent in real time, handles even noisy audio, and pushes orders directly into your operational stack.
Before diving into AI voice ordering system architecture and use cases, it helps to clarify the biggest 3 advantages you gain:
- Lower operational stress during peaks, because the AI never calls in sick or rushes a call
- Always-on availability that turns late-night or overflow calls into confirmed sales instead of missed opportunities
- Data-rich interactions—call recordings and transcripts feed your analytics stack and loyalty programs effortlessly.
After just a few weeks, you discover that your phones are no longer a bottleneck but a high-conversion sales channel guided by conversational AI.
How AI Phone Ordering Works (In Simple Terms)
Once you connect an AI phone ordering system to your business line, every incoming call follows a clear, automated path that feels effortless to guests and highly efficient to you. At a high level, here’s how the conversation unfolds from the very first ring to the final confirmation.
- A Call Comes In
The guest dials your standard phone number. Instead of a human greeting, a natural-sounding phone ordering AI agent picks up immediately. - The AI Understands the Request
As the conversation progresses, the multimodal large language models convert live audio into meaning, detecting whether the caller wants to place an order, book a table, or ask for operating hours. - The AI Responds Naturally
A lifelike synthetic voice confirms items, asks clarifying questions, and copes with accents or background noise. Multiple languages and voice personas are optional to fit your brand. - The Order or Request Is Processed Automatically
When details are confirmed, the assistant pushes data into your POS or PMS, applies loyalty points, or triggers a confirmation text. - Results Arrive—Without You Lifting a Finger
No wait time for the guest, no manual typing for staff, and zero missed calls. If anything unusually complex happens, the conversation escalates to a human instantly.
By the end of the call, you capture a clean order or reservation while your front-of-house team focuses on on-site service. That’s the core promise of an automated voice ordering system delivered over a familiar phone line.
The same workflow also underpins advanced tasks—recalling past favorites, upselling menu pairings, or routing VIP callers to senior staff. Everything depends on how you orchestrate integrations and business rules.
The Strategic Value of AI Phone Ordering
Operational efficiency used to hinge on hiring and training phone staff. Now you outsource low-value repetition to AI and free up humans for higher-touch interactions. Eliminating transcription mistakes, busy signals, and long holds directly lifts revenue, especially when upsell prompts are embedded into the dialog flow.
Beyond obvious savings, there is also a long-term brand payoff. Callers experience a consistent tone, instant response time, and zero friction day or night. That reliability builds trust much faster than a shifting pool of temporary staff ever could.
Whenever you need proof, your performance dashboard shows call-completion rates, add-on revenue, and customer-satisfaction scores improving side by side.
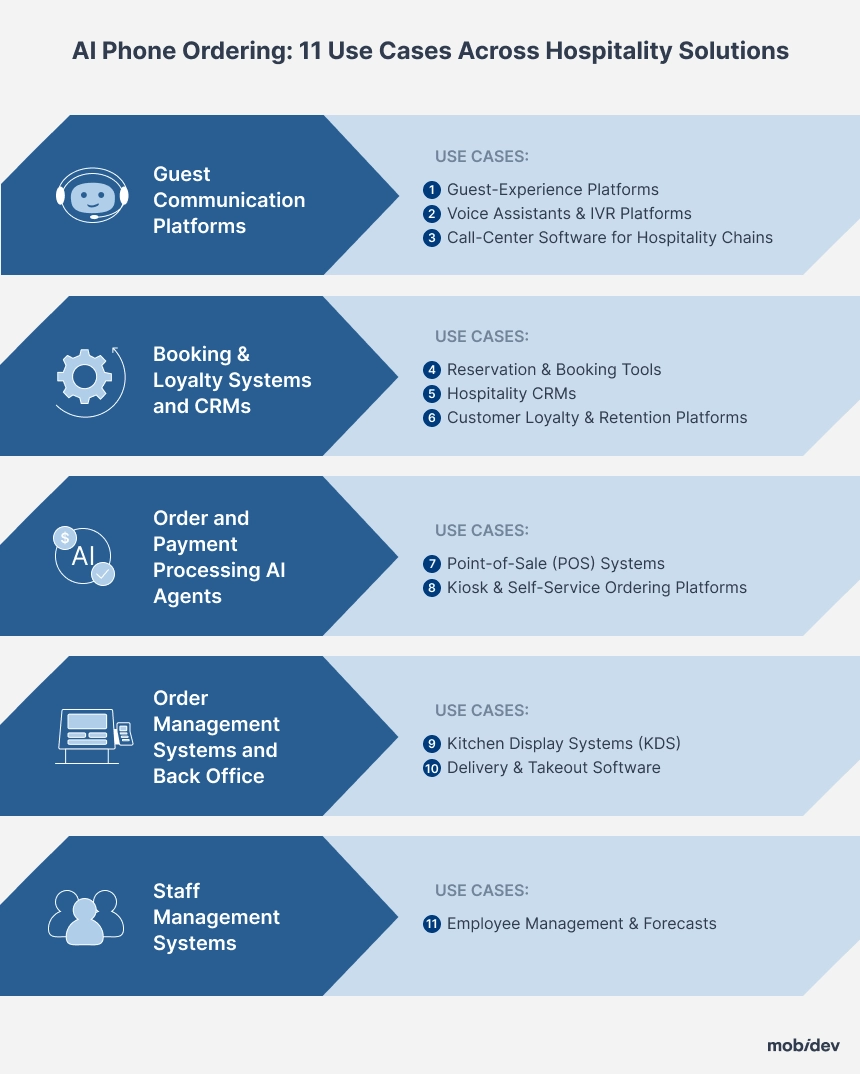
AI Phone Ordering: 10 Use Cases Across Hospitality Tech Solutions
AI voice ordering isn’t just a standalone tool—it strengthens almost every platform that keeps a modern restaurant or hotel running. To show the full picture, the scenarios below follow the outline’s functional groups and drill down to the specific subsystems that benefit most.
Group 1. Guest Communication Platforms
AI phone ordering creates a consistent, always-on first impression. From the opening greeting to the final farewell, the voice channel feels like a live concierge—yet it scales far beyond what human teams can handle.
At ShopTalk Europe 2025, many speakers talked about the importance of building a connection with customers. It is also applied in hospitality software development. An AI phone ordering system integrated with your customer data hubs can personalize communication as it seemingly effortlessly remembers guests’ preferences. It will make your guests feel special, strengthening the connection between your brand and your guests.
Use Case #1: Guest-Experience Platforms
When you embed an AI voice ordering system inside a guest-experience suite, each call becomes an instant concierge moment. A boutique hotel can greet callers by name, answer FAQs, and even confirm a spa appointment—all without tying up the front desk. The data flows into the guest profile in real time, so the next interaction, whether online or on-site, feels equally personal.
Use Case #2: Voice Assistants & IVR Platforms
Traditional IVRs frustrate callers with rigid menus; adaptive AI agents for hospitality replace button-pushing with free-form dialogue. A traveler can simply ask, “Do you have any rooms with a sea view next weekend?” and receive an immediate answer. By removing friction, you shorten call times and lift conversion rates while protecting staff from repetitive queries.
Use Case #3: Call-Center Software for Hospitality Chains
Large brands field thousands of routine questions about loyalty points, breakfast hours, or parking fees. An AI restaurant host now absorbs that volume and forwards only edge-case or VIP matters to human reps. The result is shorter queues, higher upsell success, and happier agents. Crisp transcription is vital here, so review the practical guide to building a robust speech recognition system before you fine-tune prompts for regional accents.
Group 2. Booking & Loyalty Systems and CRMs
Because the phone number doubles as an identifier, the AI phone ordering agent greets returning guests by name, references past preferences, and applies rewards automatically.
Use Case #4: Reservation & Booking Tools
Voice AI connects to your booking engine so guests can reserve a table or room at any hour. A restaurant chain, for example, lets callers secure a table even if they call at 3 a.m.; the AI checks live availability, confirms the reservation, and emails a receipt—all without human intervention.
Use Case #5: Hospitality CRMs
When a loyalty member calls, the AI recognizes the profile, suggests favorite items, and logs every detail back into the CRM. A returning guest might hear an AI Phone agent for restaurants say, “Would you like your usual oat milk latte today?” The order, payment, and feedback all sync behind the scenes, making manual entry obsolete.
Use Case #6: Customer Loyalty & Retention Platforms
AI voice workflows also turn first-time callers into long-term members. During checkout, the agent can say, “Shall I enrol today’s purchase in our points programme?” A single “yes” adds the caller to your retention funnel and boosts repeat spend without extra paperwork.
Group 3. Order and Payment Processing AI Agents
Fast-casual and QSR operators juggle POS screens, card readers, and ringing phones. A voice AI food ordering layer turns the phone line into a parallel kiosk—ideal for drivers on the road, elderly patrons, and anyone who prefers speech over taps.
Use Case #7: Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems
Picture a busy lunch rush: an AI phone ordering flow queues callers virtually, records their custom orders, and injects tickets directly into the POS. Even if the dialogue lasts a few seconds longer than a seasoned cashier, simultaneous handling of multiple lines eliminates bottlenecks.
Use Case #8: Kiosk & Self-Service Ordering Platforms
Voice AI functions as a virtual kiosk for off-premise guests. A food-court vendor can let callers navigate the same digital menu available on site, then pick up meals without ever touching a screen. Accessibility improves dramatically for guests who can only order by phone.
Because payments travel through tokenized links or saved cards, no credit card numbers echo across the dining room. Tying the voice channel into broader restaurant software development efforts—mobile wallets, self-checkout kiosks, QR menus—create a friction-free ecosystem where every endpoint shares the same menu logic, inventory counts, and promotional rules.
Group 4. Order Management Systems and Back Office
Phone orders belong in the same kitchen queue as web or kiosk transactions. Direct integration ensures timing parity, reduces miscommunication, and keeps allergy notes intact. A delivery-first pizza brand can funnel phone-in orders into a central dashboard, apply identical prep timers, and assign drivers automatically, guaranteeing consistent SLAs across all channels.
Use Case #9: Kitchen Display Systems (KDS)
The moment an AI assistant confirms an order, the ticket appears on kitchen screens with full modifiers, eliminating handwriting errors and saving precious minutes during peak periods.
Use Case #10: Delivery & Takeout Software
Once an address and payment are clear, the AI hands off the order to a dispatch tool that pings nearby couriers in real-time. Drivers see phone orders exactly like app orders, so fulfillment remains smooth and auditable.
Group 5. Staff Management Systems
Labor forecasting improves when phones stop stealing minutes from the front of house. With the AI handling routine calls, workforce-management tools enjoy a lower call burden and recommend leaner schedules. A coffee-shop chain often drops one host per shift without sacrificing service levels, reallocating hours to table touches and upsell coaching—tasks that drive higher tips and stronger online reviews.
AI phone ordering threads through guest communication, bookings, payments, kitchen workflows, and labor planning. That tight weave proves the technology is no longer a pilot experiment but a core pillar of competitive, future-proof hospitality operations.
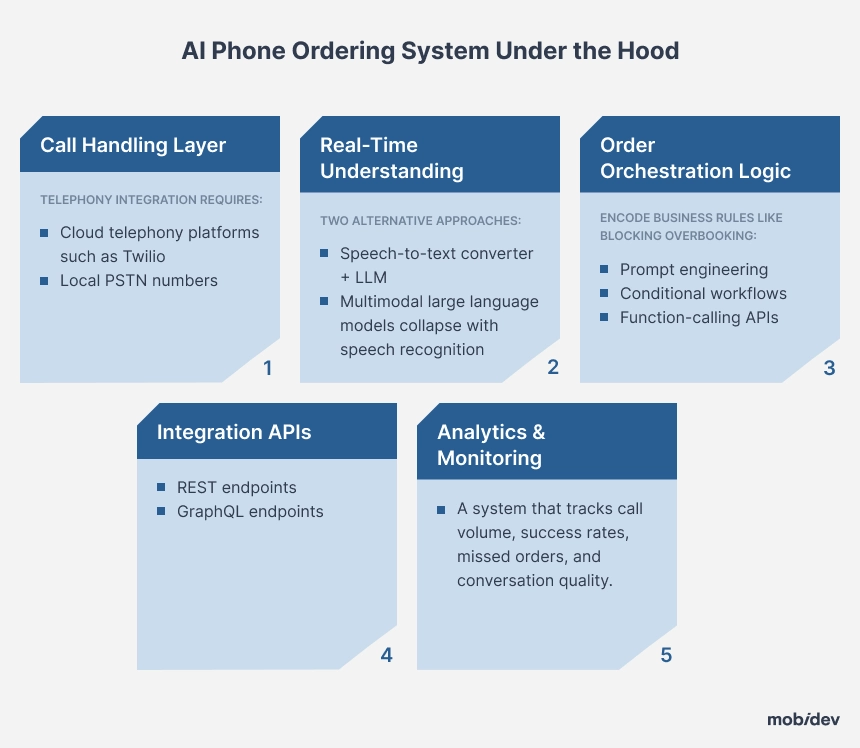
What Makes an AI Phone Ordering System Tick
Beneath every friendly greeting from an AI phone agent lies a layered architecture that never stops working. When you understand how the engine is assembled—telephony, large language models, orchestration logic, integration pipes, and analytics—you can judge vendors on substance rather than slick demos. The short tour below explains each block in practical terms and shows how they fit together to deliver a rock-solid guest experience.
1. Call Handling Layer — Telephony Integration
AI can’t start talking until the call is captured. Cloud telephony platforms such as Twilio, bridge your public phone number and the AI runtime, translating analog voice into secure VoIP streams. Local PSTN numbers for every market keep latency low, satisfy telecom regulators, and prevent those “international surcharge” surprises that drive callers away.
Inbound traffic is routed to the assistant within milliseconds, while outbound confirmations reverse-flow through the same carrier, so guests never sense they’re leaving the ordinary phone network. For multi-venue brands, fail-over rules can redirect traffic to a backup region or a live operator when cloud nodes go dark, guaranteeing uptimes that a legacy PBX could never match.
2. Multimodal LLMs — Real-Time Understanding
There are two approaches to speech recognition:
- Traditional pipelines that convert speech to text, deliver the text to an LLM, which then generates a voice response
- Multimodal large language models collapse those steps: raw audio in, meaning and response out. Because acoustic cues such as pitch and hesitation remain in context, the AI detects impatience or confusion and adapts its tone on the fly.
This single-pass design matters when blenders roar in a smoothie bar or when a driver phones from a noisy delivery van; the assistant still grasps “half-sweet mango, no ice” without a second guess.
3. Order Orchestration Logic — Business Rules in Motion
A phone order is more than transcribed words; it’s a contract that must honor menu limits, pricing policies, and kitchen capacity. Orchestration logic enforces those rules in real-time. If a caller asks for a gluten-free base that has just sold out, the AI can immediately propose an alternative.
When reservations creep beyond a room’s turnover buffer, the same layer blocks the overbooking before it reaches the PMS. In practice, you encode these rules with prompt engineering, conditional workflows, or function-calling APIs exposed by the model—whichever fits your stack and talent pool.
4. Integration APIs — Connecting the Tech Estate
Even the most eloquent AI falls flat if it can’t push data into the systems you already trust. REST and GraphQL endpoints turn spoken instructions into POS line items, CRM events, or loyalty point updates. Webhooks reverse the flow, letting the assistant notify the caller that an order left the kitchen or that a table is ready.
A unified schema across channels—voice, kiosk, mobile—eradicates mismatched modifiers and ensures that allergy flags marked by phone propagate to kitchen screens just as they would from an app.
5. Analytics & Monitoring — Closing the Feedback Loop
Once hundreds of calls roll in daily, insight beats intuition. Dashboards slice volume by the hour, track average handle time, and flag spikes in “Agent, please” transfers that hint at training gaps. Drill-downs reveal which accents or phrases still stump the model, guiding your next fine-tuning cycle.
Real-time alerts can even ping a supervisor when a VIP caller is detected, prompting proactive white-glove service. Continuous monitoring turns the AI from a static tool into a living system that evolves with your menu, your brand voice, and your audience.
Need a deeper architectural walkthrough—including sample tech stacks, RAG patterns, and deployment tips? The knowledge hub on AI in hospitality outlines integration best practices, while the step-by-step CTO’s guide to developing AI agents for hospitality unpacks orchestration choices, cost models, and governance practices so your phone agent launches fast and scales safely.
Why the Timing Matters Right Now
Global hospitality AI spend continues to climb, with market volume projected to hit $1.46B by 2029—an impressive 57 % CAGR, according to the Global Artificial Intelligence in Hospitality Market Report 2025. Concretely, that means early adopters are locking in efficiency gains and guest-experience differentiation while late movers scramble to catch up.
You don’t have to overhaul your entire tech stack on day one. Many operators start by automating off-peak calls or overflow queues. Even a modest pilot of AI food ordering for restaurants can reveal immediate savings once you see how many calls are answered instantly instead of dropping to voicemail.
Tech providers, meanwhile, discover additional revenue streams by bundling AI phone ordering system features into their SaaS platforms. Whether you build the feature set in-house or leverage external APIs, your customers increasingly expect phone-based conversational AI as a default.
To map out the cost/benefit equation and align AI investment with your broader goals, consider tapping into specialized AI consulting services. Expert guidance helps you determine realistic ROI thresholds and avoid scope creep before writing a single line of code.
Implementation Challenges of an AI Voice Ordering System
AI brings transformative power, but deployment is never plug-and-play. Real success stems from acknowledging obstacles early and designing mitigations.
Common AI Implementation Challenges
A large-scale Danish study involving 25,000 workers and 7,000 firms recently found only modest productivity gains (~3 % time savings) from generic chatbots, echoing the classic productivity paradox: technology alone rarely transforms outcomes until paired with deeper workflow redesign and upskilling. That insight applies equally to AI restaurant host deployments; you must coordinate process change, staff training, and monitoring to unlock the full potential.
Change management is therefore paramount. Position AI as a stress-relief tool, not a threat. When staff see fewer error-prone calls and more meaningful guest interactions, adoption climbs naturally.
For Hospitality Operators
You likely juggle multiple vendors—your POS, a table-management app, a loyalty platform. The AI ordering system must integrate, not replace, those tools. Guests who dislike bots should still reach a human on request, and the new system must prove ROI quickly.
For SaaS Providers
Processing voice data triggers privacy obligations under GDPR or CCPA. On top of that, accurate domain-specific understanding (“skin-on fries”, “split check”) demands careful prompt engineering or RAG pipelines. Multilingual support and edge-case error handling round out a sizable technical backlog.
How to Build an AI Calling Agent: Step-by-Step Roadmap
Proper project planning boosts success odds. You should:
- Define Strategy & Use Cases – Pinpoint peak-hour pain or after-hours missed calls.
- Evaluate Vendors or Design Architecture – Check language coverage, telephony support, and analytics depth.
- Integrate & Configure – Wire the agent to POS, booking, and CRM endpoints.
- Test & Optimize – Run pilots, tweak dialog prompts, adjust failover rules.
- Roll Out & Train Staff – Teach teams to monitor dashboards and step in during escalations.
- Iterate Continuously – Feed real-world data back into model tuning and menu updates.
Building AI Phone Ordering Software with MobiDev
You can design an end-to-end solution or integrate third-party voice APIs into your existing stack—the choice depends on budget, timeline, and internal expertise. Either way, your best-case outcome is the same: callers enjoy frictionless ordering while your staff focus on hospitality excellence.
By engaging a specialist team that delivers comprehensive AI agent development services—you tap into production-ready expertise across cloud telephony, LLM fine-tuning, and hospitality domain logic. You receive guidance on regulatory compliance, multi-system APIs, and ongoing model refinement without diverting core resources.
Whether you operate a single venue or develop SaaS platforms for thousands, an AI voice ordering agent positions you for growth, resilience, and brand loyalty long after initial deployment.