Contents:
Businesses are always looking for ways to stay agile in a fast-paced environment. With the introduction of artificial intelligence, most organizations have experimented with AI-powered chatbots, data analysis, or process automation. Yet AI encompasses far more than simple Q&A or static recommendation systems. Agentic AI—sometimes referred to as Agent AI—takes this further by shifting toward software that observes and acts on its own.
My name is Iurii Luchaninov, and I am a Solutions Architect with 20 years of experience in merging innovative architecture with pragmatic business solutions. In this article, I will explain what Agentic AI is, highlight its most critical use cases, and provide guidance on how businesses can harness AI agents to revolutionize legacy systems, outpace competitors for SaaS platforms, or turbocharge in-house software.
We will keep it straightforward enough for those exploring Agentic AI from a strategic perspective, yet offer enough depth to give actionable insights for leaders looking to dive deeper. By the end of this article, you will have a solid grasp of what Agentic AI is capable of and a clear sense of the next steps if you are considering an AI-led transformation for your business.
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI is more than a catch-all phrase. It is a framework for artificial intelligence in which software agents can perceive, plan, and act on their own in pursuit of a target. Rather than sitting idly by, waiting for a prompt from a user, these AI agents detect changing conditions and adjust their behaviors to meet particular goals.
The market value of agentic artificial intelligence in 2024 was $5.1B, and by 2030, it is projected to reach 47.1B due to a 44% CAGR. These figures reflect the actual value that business organizations, educational institutions, and research organizations in tech assign to autonomous decision-making systems. Whether the task is to enhance a CRM platform or automate a legacy process, agentic AI systems can bridge the gap between static code and dynamic, self-guiding applications.
Agentic AI Definition
Essentially, Agentic AI is a programmed intelligent agent capable of designing its own course of action to resolve a problem. This means looking at information from its environment, making decisions based on internal deliberation, and adapting based on fresh feedback. When answering the question, “what is agentic AI?” and questions about how it is not just a generic chatbot or ML model, the answer is that it all comes down to proactivity and autonomy. These AI agents don’t simply return a pre-scripted reply; they can cooperate, delegate tasks to sub-agents, or alter their process mid-task if conditions change.
By extension, if you ask yourself, “What is an AI agent in simple terms?” think of software that works almost like a junior colleague: it receives a goal, analyzes incoming data, and makes decisions based on that data.
Agentic AI vs Generative AI
Modern AI is typically grouped into overarching paradigms. Two of today’s most prominent paradigms are Agentic AI and Generative AI. Although both are cutting-edge, it is critical to grasp their specific roles:
- Generative AI creates new content—text, images, code—based on patterns it has learned.
- Agentic AI is about decision and autonomy: the software acts without having to wait for a command.
That is to say, Agentic AI doesn’t just “respond to questions” or “generate designs.” It has a purpose in mind and acts toward achieving it. By contrast, Generative AI is well suited to creative production yet remains reactive; it must be prompted or stimulated before it can generate something new.
Here is a brief comparison:
| # | Feature | Generative AI | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Structure | AI that generates new content based on learned patterns | System with Gen AI or other type of AI at its core that makes decisions |
| 2 | Primary Function & Objective | Analyses unstructured data and produces novel content | Operates autonomously and makes decisions, completes multi-step tasks with minimal human guidance |
| 3 | Level of Autonomy | Low – requires prompts or user inputs | High – runs independently |
| 4 | Typical Applications | Analysis of the unstructured data, content generation, design, text/image/video creation | Workflow optimization, decision-making, automation |
| 5 | Key Technologies | Large Language Models (LLMs), GANs, Diffusion Models | Augmented LLM, LangChain (Python/NodeJS), Amazon Bedrock, Rivet, Vellum |
A more accurate way to distinguish Agentic AI from Generative AI is that Agentic AI makes decisions and takes actions autonomously, while Generative AI focuses on producing content or novel outputs without making decisions. Both rely on data — sometimes explicitly provided, sometimes embedded within the model — but the key difference lies in autonomous decision-making.
Types of AI Agents
The various forms that such software takes are referred to as the types of AI agents. They include:
- the reactive agents that respond to the immediate input without remembering too much context
- model-based agents that plan by means of internal representations of the world
- more advanced hybrid models that combine learning, planning, and remembering.
Several different frameworks for AI agents exist to help developers design the best AI agents for a given application. These frameworks typically define how the agent receives inputs (e.g., user data, sensor data, or logs), processes them, and decides on the best action to take.
As businesses expand, they graduate to more sophisticated AI systems than mere rule-based chatbots. Some rely heavily on machine learning to identify the sentiment of the user, and others apply reinforcement learning to learn decision-making strategies over a period of time. The end goal remains the same: to create an AI agent that reduces the need for human intervention on an ongoing basis.
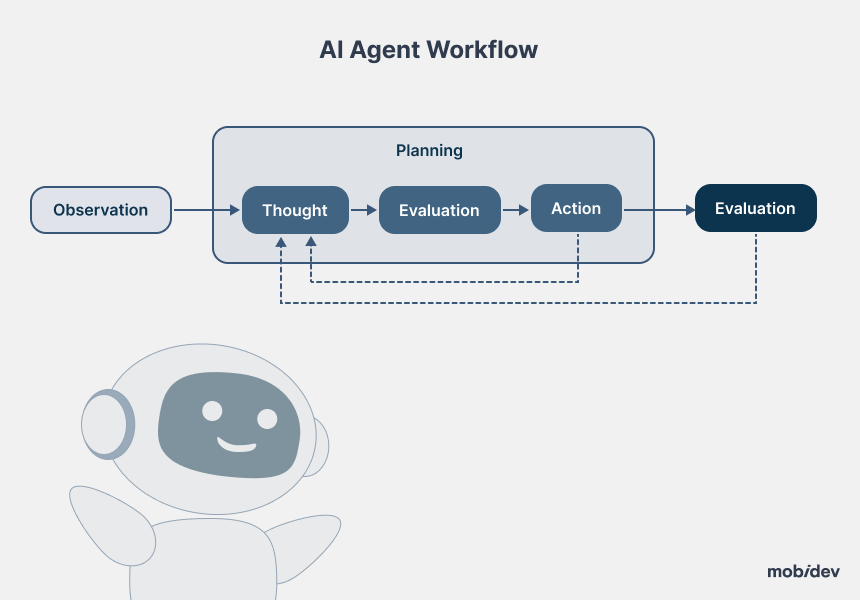
How AI Agents Work: A Look Under the Hood
Current AI trends incorporate different technologies to deliver context-sensitive conversation, data analytics, and autonomous action. Agentic AI chatbots, for instance, now rely more on multi-agent architectures. A front-end “proxy” receives input, and then calls on specialist sub-agents—writing, research, or translation modules, for instance—to produce sophisticated outputs.
This multi-agent setup provides chatbots with the capability to carry out tasks on their own. As the user requests an email campaign, the front-end agent allocates tasks to other agents (drafting, editing, fact-checking).
AutoGen Studio, AutoGPT, and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) are a few systems that enhance their capabilities by combining large language models with external data sources. The chatbot is then able to supply accurate, situation-specific answers with fewer errors or “hallucinated” content.
In practice, AI agents can be powered by various technologies, depending on the use case. Here are just several examples:
- Machine Learning (ML) for predictions and continuous improvement
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) to comprehend user requests and respond with human-like answers
- Computer Vision for extracting information from image or video data
- Reinforcement Learning (RL) enhances decision-making by trial and error
- Knowledge Graphs & Semantic Search for quick retrieval of context-aware information
- Generative AI & Large Language Models (LLMs) that produce coherent text, images, or code at scale
- Autonomous AI & Multi-Agent Systems that collaborate on complex tasks.
Key 5 Business Benefits of Agentic AI
Why is Agentic AI becoming a top priority for so many businesses? The reasons stem from automation, cost efficiency, and the ability to refine decision-making processes continuously. Agentic AI also boosts software longevity, since solutions that adapt on their own won’t become irrelevant as quickly in fast-paced markets.
- Elevated Automation
By transferring repetitive work—like answering common inquiries or updating records—to AI agents, teams reduce manual workloads. This efficiency is particularly impactful when scaling an application or handling seasonal spikes in demand. - Real-Time Intelligence
Traditional software usually processes data in batch mode or triggers tasks based on scheduled events. Agentic AI, however, thrives on real-time inputs, adjusting its strategies in the moment. This capability means fewer delays, more dynamic risk assessment, and immediate user feedback loops. - Personalized Interactions at Scale
Agents that integrate learning mechanisms and user data can provide hyper-tailored recommendations, ensuring each interaction feels relevant and immediate. Whether it’s a retail chatbot that knows your shopping preferences or a knowledge base that modifies its suggested articles to match your department’s needs, personalization improves experiences. - Better Cost Control
As teams delegate more tasks to AI, support and overhead costs are reduced. Operations that once took multiple staff hours—like manually sorting data or triaging customer complaints—can be processed autonomously, freeing up resources for strategic innovation. - Adaptive Enhancements Over Time
Although fully “self-learning” systems are still limited in scope today, AI agents can often be updated via new data sets or expansions of existing knowledge bases. When organizations keep humans in the loop—by reviewing outcomes or providing additional training data—agents can gradually improve their performance. This reduces errors and fosters an environment where each iteration of your software delivers more accurate results.
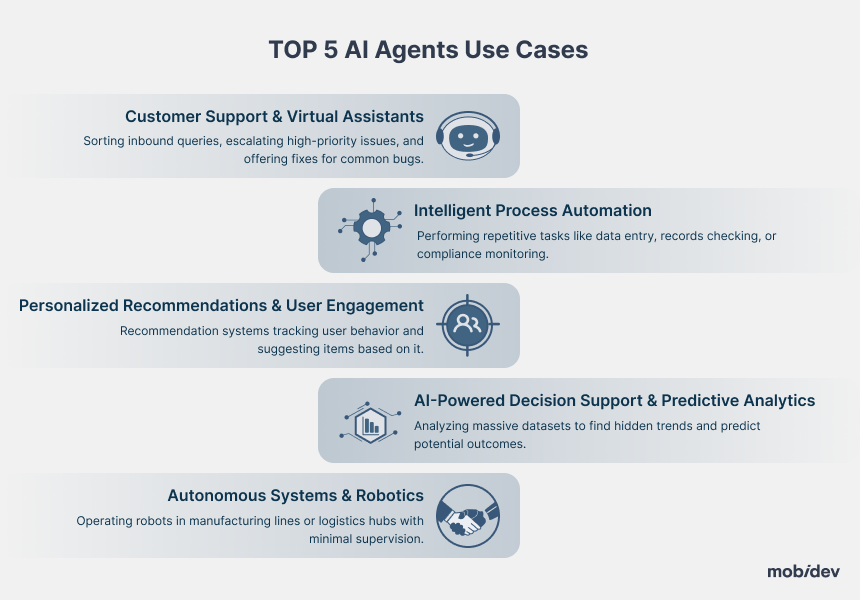
TOP 5 AI Agents Use Cases
Agentic AI is adaptable across a wide array of sectors. Below are some prominent AI agents useful case scenarios where organizations deploy these technologies for tangible gains.
1. Customer Support & Virtual Assistants
Companies integrate AI agent chatbots or voice assistants that not only answer FAQs but also handle more complex tasks—like checking account statuses or scheduling appointments. Imagine a SaaS tool that uses an autonomous agent to sort inbound queries, escalate high-priority issues, and even propose immediate fixes for common bugs.
2. Intelligent Process Automation
Repetitive workflows such as data entry, records checking, or compliance monitoring become prime candidates for an intelligent agent in AI. In the finance sector, an AI agent can quickly validate claims or transaction histories, reducing the burden on human auditors.
3. Personalized Recommendations & User Engagement
Many organizations now see personalization as central to user satisfaction. AI agents examples include e-commerce recommendation systems that track browsing behavior and suggest items based on your style, or streaming services that curate unique content feeds.
4. AI-Powered Decision Support & Predictive Analytics
In data-heavy industries, an AI agent can sift through massive datasets to surface trends and potential outcomes. For instance, a logistics company might rely on predictive agents to anticipate shipping delays. A healthcare service could use an intelligent agent to analyze patient data for early diagnostic patterns.
5. Autonomous Systems & Robotics
Agentic AI isn’t confined to chat or data analysis. Robots in manufacturing lines or logistics hubs can operate with minimal supervision, navigating dynamic warehouse environments, optimizing routes, and coordinating with other machines.
Industries Leading the Adoption of Agentic AI
Some sectors are further ahead than others in adopting Agentic AI. Below is a quick snapshot of where these technologies are currently making waves:
SaaS & Software Development
In these environments, AI agents automate workflows, optimize cloud resources, and boost personalization.
Use Case: Customer support chatbots that learn from repeated user tickets, plus embedded automation for dev-ops tasks.
Retail & Hospitality
AI agents in retail enhance product recommendations, pricing, inventory management, customer support, and fraud detection, while hospitality businesses streamline guest interactions, reservations, personalized offers, and menu ordering or delivery.
Use Cases: Personalized shopping assistants, AI-driven inventory and demand forecasting, dynamic pricing optimization, virtual concierges for hotels, and automated order management systems.
Health & Wellness
AI focuses on continuous monitoring, early detection, and user-specific wellness suggestions.
Use Case: A fitness app that dynamically adjusts workout plans based on performance metrics, stress levels, or user feedback.
Finance & Banking
Fraud detection, risk scoring, and real-time advisory services harness agentic AI’s speed and adaptability.
Use Case: AI-driven financial assistants or watchful transaction monitoring that detects unusual activity within seconds.
Logistics & Manufacturing
Supply chain operations, predictive maintenance, and autonomous navigation benefit from agentic AI solutions.
Use Case: Factory robots that move goods, restock supplies, and coordinate with other equipment to prevent collisions.
Agentic AI for Different Business Types
Different organizations have different aims and challenges in the integration of AI. They vary from scaling new SaaS platforms with intelligent capabilities to transforming existing infrastructures run on legacy systems. In spite of the differences, Agentic AI always offers ways of reducing human overhead, enhancing decision-making, and strengthening the user experience.
AI-Powered Software Startups
Many AI startups have to balance the cost of computing, choose the appropriate AI tools, and scale fast. Agentic AI enables this by giving them self-improving processes right out of the box, which eliminates tedious manual workflows and enables lean teams to focus on enhancing and evolving the product.
Mature SaaS Companies Enhancing AI Capabilities
Tight customer retention, operational efficacy, and the need for perpetual innovation are the common problems of established SaaS businesses. Agentic AI resolves these by simplifying user interactions and scaling predictive analytics to provide personalized experiences at scale. The blend also allows for effective internal workflows, supporting steady but forward-looking development approaches.
Companies with In-House Software
Organizations with proprietary systems need to address issues of AI knowledge gaps, data security, and ROI. They seek to use existing data to streamline processes with the help of Agentic AI, with on-premise deployments to secure sensitive information. The outcome is faster decision-making with stringent compliance that fosters trust internally as well as externally.
Pioneer Software Companies Updating Legacy Products with AI
Companies operating on legacy architectures struggle to integrate across silos and manage complex integrations. Agentic AI introduces intelligence into legacy architectures in the form of automation and real-time guidance without the need for a full re-architecture. Such a reimagining brings new life to proven solutions, rendering them relevant and competitive in modern environments.
3 Common Myths & Key 5 Considerations for Adopting Agentic AI
As more individuals gain an interest in what agentic AI is and how it will reshape the nature of modern software, misconceptions, and practical obstacles inevitably ensue. Dispelling these misconceptions lays the groundwork for successful deployments for your business.
Myth #1: Agentic AI Is Too Expensive and Complex
One of the most widespread worries is that agentic AI is too pricey for anything but the largest enterprises. In reality, the cost and complexity vary depending on your requirements. Low-scale deployments—e.g., an AI agent to automate help-desk processes—can start with existing libraries and cloud-based APIs. You could integrate an intelligent AI agent with little upfront investment if you utilize proven frameworks that do a lot of the heavy lifting.
For large businesses that have huge streams of data or advanced analytics, of course, the initial engineering cost is higher. But the ROI typically outweighs that cost: automated processes, reduced staffing burdens, and faster decision-making cycles yield massive cost savings and new revenue streams in the long term.
Myth #2: Agentic AI Will Take Over All Human Functions
Job loss is generally an issue that arises in discussions about advanced AI. However, AI agents have the edge in terms of continuous monitoring, fast examination of data, or repetitive tasks. They excel in niche applications like the detection of anomalies or the management of queues. Meanwhile, human beings retain a monopoly on creativity, strategic thinking, and empathetic stakeholder communication.
Think about how digital transformations have taken place in the past: new technology alters the nature of the job rather than obliterating it. Workers freed of mind-numbing duties can shift toward jobs that demand relationship-building, imagination, or high-level management. Ultimately, agentic AI systems that have been carefully designed complement the human workforce, producing better results for workers and end-users.
Myth #3: Plug-and-Play AI Agents Cure Everything Overnight
It is also the case that open-source and commercial platforms speed development. However, AI agent frameworks need to be configured, and data must be cleansed, integrated into existing workflows, and maintained. Agentic AI is not a fix-it-and-forget-it affair. It is a practice that needs to be closely monitored on a regular basis and tweaked step by step.
Businesses can begin with a minimal agent to tackle a single workflow and increase the agent’s capabilities as they iterate on the training data or identify new tasks. Over months and years, AI has become a more sophisticated solution that tackles more challenging problems, but it is a process. Expect a learning curve, especially if you have plans to integrate the agent deeply into your enterprise infrastructure.
Key Considerations
- Data Governance & Security. AI performance depends on the quality and accessibility of data. Make sure your data pipelines are reliable, secure, and compliant with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. This becomes especially critical for companies with in-house software that handle sensitive user information.
- Aligning with Business Strategy. Agentic AI should not be an isolated experiment. Tie any implementation to clear objectives—cost savings, increased user engagement, or modernization of a legacy platform.
- Team Buy-In & Skill Gaps. Introducing AI can provoke skepticism or fear among team members. Early education and open communication about the role of AI fosters acceptance. For advanced tasks, organizations might seek external experts or specialized AI consulting to fill internal skill gaps.
- Balancing Autonomy with Oversight. While the hallmark of Agentic AI is independence, all solutions need guardrails. Define escalation points or triggers for human intervention when the agent faces ambiguous data or high-stakes decisions.
- Measuring Impact. Establish clear KPIs or metrics from the start. A SaaS product might track churn reduction or user satisfaction. A healthcare system could monitor diagnosis accuracy. By measuring outcomes, you can refine your AI agents continually.
With these insights, businesses and researchers stand a better chance of making agentic AI work smoothly. Proper planning and stakeholder alignment turn potential challenges into opportunities for innovation.
Getting Started with Agentic AI
Once you’re ready to explore Agentic AI more concretely, it helps to follow a structured approach:
- Identify AI Integration Opportunities
Evaluate which tasks or departments can benefit most from automation or data-driven decision-making. Is it customer onboarding, dynamic resource allocation, or real-time anomaly detection? Pinpointing these focus areas early prevents random experimentation and helps you deploy AI agents in a strategic manner. - Compare Custom AI Development vs. Consulting Services
Not every organization has in-house data scientists or AI specialists. In such cases, external advisors can offer a roadmap to deploy an AI agent effectively. However, building custom solutions often yields higher returns. You can tailor the software to match unique workflows, data ecosystems, and branding considerations. - Create an AI Adoption Roadmap
Laying out a phased strategy prevents scope creep and confusion. Start with a pilot project in one domain—say, an AI agent that automates inbound support tickets. Prove its value, then expand to handle more tasks or integrate a broader range of data sources. This incremental rollout is particularly relevant for pioneer software companies modernizing legacy products that must validate each step. - Evaluate Tools & Frameworks
Numerous open-source libraries (like LangChain, SmallAgents, AutoGen) and commercial solutions can jumpstart your effort, especially when you’re learning how to build AI agents. Depending on your goals, you might also use “all-in-one” AI platforms. The key is aligning with your operational model: some tools cater to quick prototypes, while others are designed for enterprise-scale reliability. - Establish Continuous Learning & Improvement
Agentic AI doesn’t end upon launch. Like any complex system, it needs monitoring, retraining (if applicable), and periodic updates. Whether you integrate reinforcement learning or simpler ML pipelines, plan for iteration. This ensures your AI agents maintain accuracy as market conditions shift.
If you want an in-depth blueprint on how to build an AI agent, we have a dedicated article that covers everything from conceptual design to deployment best practices. The guide highlights the typical development stages, addresses common pitfalls, and explains how to ensure your AI solution remains adaptable as your business evolves.

Ready to Incorporate AI Agent into Your Sofware?
Learn How to Build AI AgentsMain 4 Future Trends of Agentic AI
Agentic AI is taking hold but still has a long distance to travel. Almost 20 percent of businesses, for example, list data as the single largest barrier to value capture with generative AI—which is to say that as data infrastructure becomes more established, more advanced agentic solutions will gain traction.
1. Adaptive AI Through Specialized Reinforcement Learning
In certain niche applications, AI agents can use reinforcement learning to simulate and test different actions. However, it is important to clarify that AI agents do not learn from their operational decisions in real time and do not memorize previous mistakes or actions. Instead, such learning, when applied, happens in pre-defined training environments or under strict supervision. While specialized RL setups can help reduce operational friction in controlled domains, continuous self-improvement as part of day-to-day functioning is not a feature of current AI agents.
2. Explainability & Ethical AI
As businesses outsource critical workflows to autonomous systems, the demand for transparency and accountability increases. Watch for the development of new best practices, tools, and standards that support the explainability of AI agent decisions. This gives regulatory bodies, executive teams, and end users the confidence to trust the behavior of these advanced systems.
3. Integrated Ecosystems (Metaverse & IoT)
The future of “connected experiences” merges the digital with the physical. Imagine it: AI agents that manage a facility’s IoT sensors as they synchronize VR-based employee training. Through the linking of real-world objects, virtual spaces, and advanced analytics, businesses have the potential to create environments in which decisions happen with ease.
4. Strategic Planning & High-Level Coordination
In the future, agentic AI will transition away from operational duties to informing big-picture strategies. Picture a system that examines the entire supply chain, right down to the vendor prices and transportation routes, and recommends new markets to expand into or new lines of products. This transition away from tactical to strategic duties places agent AI in the role of a digital boardroom consultant.
What’s Next?
If you have kept pace with this progression from understanding what an AI agent is, to learning about Agentic AI versus Generative AI, to recognizing how wide-ranging the types of AI agents can be, you likely have concepts forming in your mind for your software ecosystem. To make those concepts a reality:
- Measure your organization’s readiness. Review your data maturity, your current IT stack, and the willingness of your leadership to invest.
- Start small with one high-impact area. Choose a project where success is easy to measure and can convince stakeholders.
- Plan for ongoing iteration. Develop feedback loops that allow your AI agents to learn through real-world interactions, adjusting to new information, or changing workflows.
- Hire expert professionals. If your team lacks particular AI expertise, consider bespoke development or consulting. The agentic nature of AI often calls for cross-functional capabilities.
As the need for Agentic AI expands, businesses that succeed in deploying these solutions will gain more than the simple productivity benefits. They’ll open the door to more resilient, more responsive applications that look forward to future problems, coordinate dynamic processes, and place them at the forefront of digital transformation. Through a thoughtful process—piloting, measurement, and iteration—your organization can unlock the complete potential of AI agent development services and lead the pack in an era of technological change.